Third Law Of Motion
Key Notes:
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Definition:
Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that forces always come in pairs.

Action-Reaction Pairs:
Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction on the first object. These forces are called action and reaction forces.

Examples:
- Walking: When you walk, your foot pushes backward against the ground (action), and the ground pushes your foot forward with an equal and opposite force (reaction).

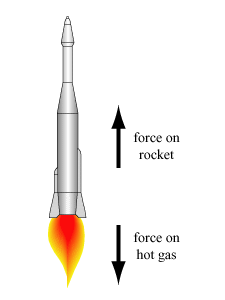
- Rocket Propulsion: In a rocket, the engines expel gas backward (action), and the reaction force propels the rocket forward.

Forces Are Equal in Magnitude:
The forces in action-reaction pairs are always equal in strength. However, they act on different objects, so they do not cancel each other out.

Forces Are Opposite in Direction:
The direction of the force exerted by the first object is opposite to the direction of the force exerted by the second object.

Impact on Motion:
The action and reaction forces do not cancel out because they act on different objects. Therefore, they affect the motion of each object involved.
Interaction with Objects:
This law explains how objects interact with each other. For example, when you push against a wall, the wall pushes back with an equal force.
Misconceptions:
It’s important to note that while the forces are equal and opposite, the resulting motion of the objects may not be the same due to differences in mass and other factors.
Let’s practice!

