Balanced And Unbalanced Forces
Key Notes:
Definition of Force
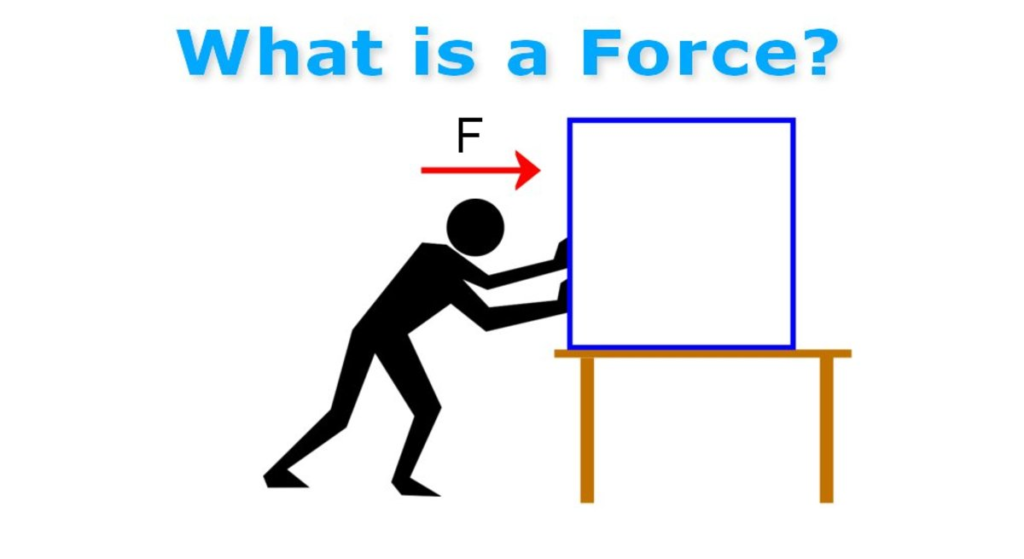
- Force is a push or pull that acts upon an object. It can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change its speed or direction.
Balanced Forces
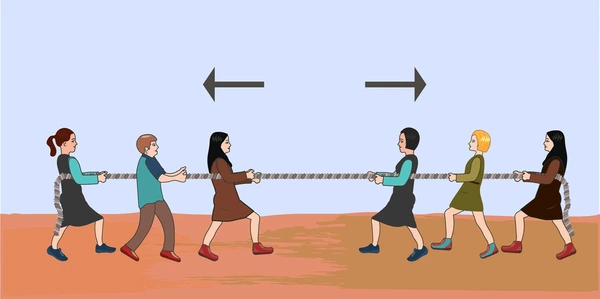
- Balanced forces occur when the total force acting on an object is zero, resulting in no change in the object’s motion.
- If an object is at rest, balanced forces will keep it at rest.
- If an object is moving, balanced forces will keep it moving at a constant velocity.
- Example: A book resting on a table experiences balanced forces. The downward gravitational force is balanced by the upward normal force from the table.
Unbalanced Forces
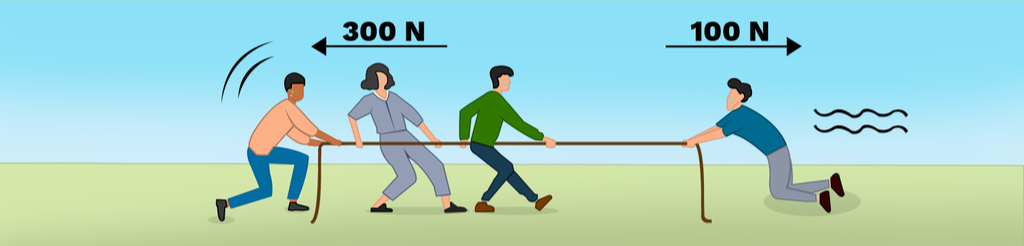
- Unbalanced forces occur when the total force acting on an object is not zero, resulting in a change in the object’s motion.
- Unbalanced forces can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction or speed.
- Example: Kicking a stationary soccer ball applies an unbalanced force, causing the ball to move.
Effects of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
- Balanced forces do not change the motion of an object; the object remains in its current state of motion (either at rest or moving at a constant speed).
- Unbalanced forces change the motion of an object, causing acceleration (a change in velocity).

Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)
- An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- This law explains the relationship between balanced forces and the motion of objects.

Examples in Daily Life
- Balanced Forces: A hanging lamp, where the tension in the cable and gravity are balanced.
- Unbalanced Forces: A car accelerating, where the engine provides a force greater than the opposing friction.
Identifying Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
- To determine if forces are balanced or unbalanced, consider the net force (sum of all forces) acting on the object.
- If the net force is zero, the forces are balanced.
- If the net force is not zero, the forces are unbalanced.

Let’s practice!

