Describing Motion
Key Notes:
Definition of Motion:
- Motion occurs when an object changes its position relative to a reference point over time.
Types of Motion:
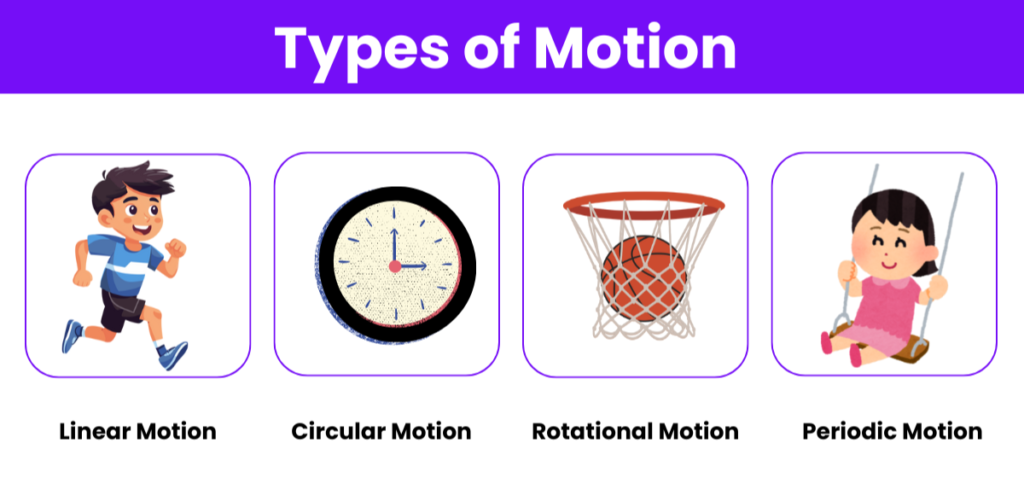
- Linear Motion: Movement in a straight line (e.g., a car moving on a road).
- Circular Motion: Movement in a circular path (e.g., the motion of a ceiling fan).
- Rotational Motion: Motion of an object around its axis (e.g., Earth’s rotation).
- Oscillatory Motion: Back-and-forth motion (e.g., a pendulum).
Reference Point:
- A fixed point used to determine the position of a moving object.
- Motion is always described relative to this reference point.
Distance and Displacement:
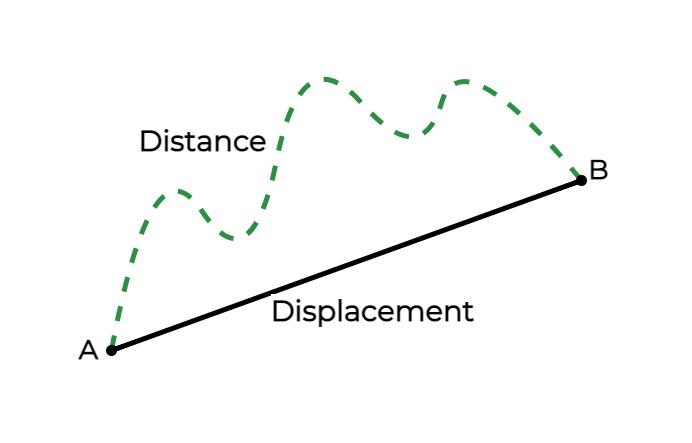
- Distance: The total path length traveled, a scalar quantity (only magnitude).
- Displacement: The shortest straight-line distance between the initial and final positions, a vector quantity (magnitude and direction).
Speed and Velocity:
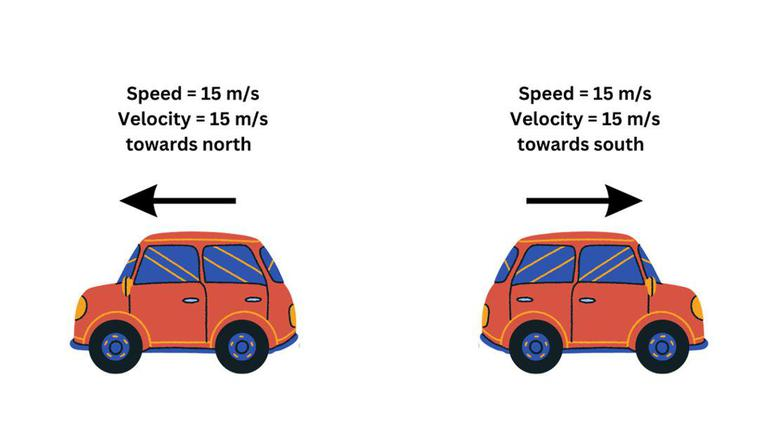
- Speed: The rate at which distance is covered (scalar quantity).
Speed = Distance / Time
- Velocity: The rate at which displacement occurs (vector quantity).
Velocity = Displacement / Time
- Uniform motion has constant speed/velocity, while non-uniform motion involves changing speed/velocity.
Acceleration:
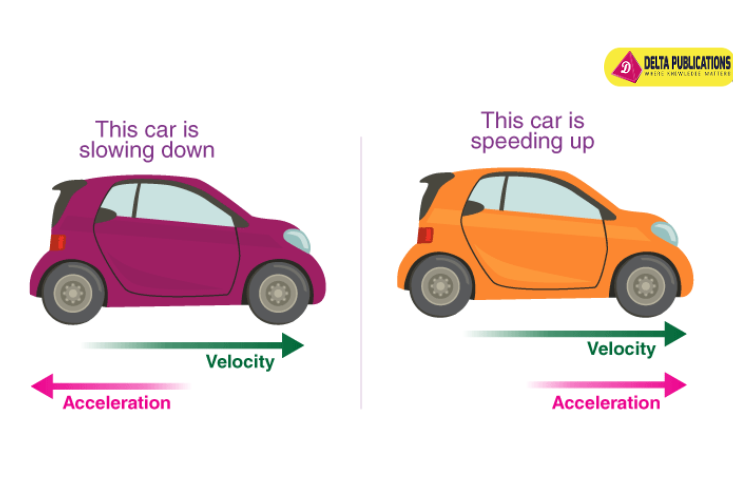
- The rate of change of velocity over time.
Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Time Taken
- Positive acceleration indicates increasing velocity; negative acceleration (deceleration) indicates decreasing velocity.
Graphical Representation of Motion:
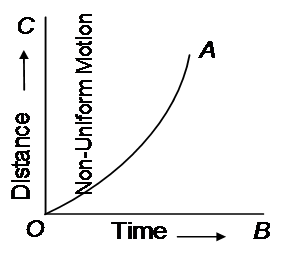
- Distance-Time Graph: Slope represents speed. A straight line indicates uniform motion.
- Velocity-Time Graph: Slope represents acceleration. The area under the graph gives displacement.
Equations of Motion (For Uniformly Accelerated Motion):
First equation: v = u + at
Second equation: s = ut + 1/2 at2
Third equation: v2 = u2 + 2as Where:
- v: Final velocity
- u: Initial velocity
- a: Acceleration
- s: Displacement
- t: Time
Relative Motion:
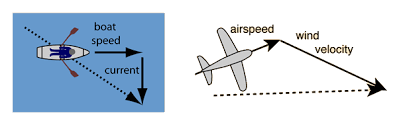
- Motion of an object observed from another moving or stationary reference point.
- Important for understanding relative speed in cases like vehicles moving in opposite or the same direction.
Examples of Motion:
- Walking, flying an airplane, Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Let’s practice!

