Plantae
Key Notes:
Introduction to Kingdom Plantae
- Plantae is one of the five kingdoms in biological classification.
- Includes multicellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Common examples: trees, shrubs, herbs, mosses, and ferns.
Characteristics of Plantae
- Cell Structure: Cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose.
- Chlorophyll: Contain chloroplasts with chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
- Reproduction: Both sexual and asexual reproduction methods.
- Nutrition: Autotrophic (synthesize food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide).
Classification of Plantae
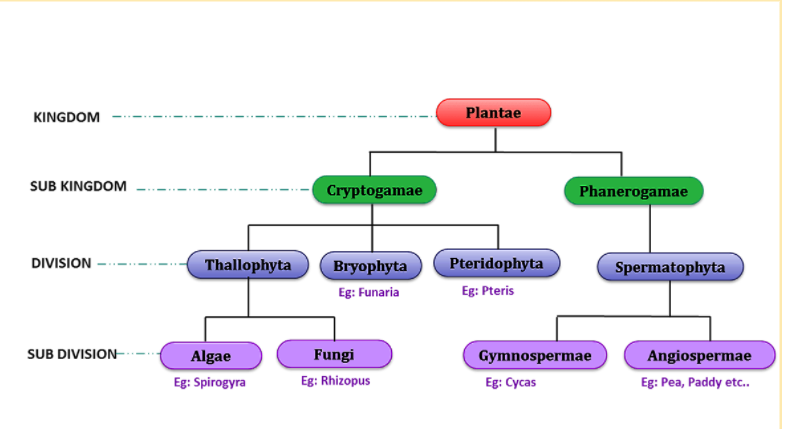
Plantae is divided into various groups based on structure, vascular system, and reproduction:
- Thallophyta:
- Simplest plants, body not differentiated into roots, stems, and leaves.
- Example: Algae.
- Bryophyta:
- Non-vascular plants, require water for reproduction.
- Examples: Mosses, liverworts.
- Pteridophyta:
- Vascular plants without seeds.
- Examples: Ferns.
- Gymnosperms:
- Vascular plants with naked seeds.
- Examples: Pine, cycas.
- Angiosperms:
- Vascular plants with seeds enclosed in fruits (flowering plants).
- Examples: Mango tree, sunflower.
Vascular System
- Consists of xylem (transports water and minerals) and phloem (transports food).
- Found in higher plants (Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms).
Significance of Plantae
- Primary producers in the ecosystem, forming the base of the food chain.
- Produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis.
- Provide food, shelter, and raw materials for humans and animals.
Adaptations
- Adapted to diverse habitats: aquatic (e.g., algae), terrestrial (e.g., trees), and extreme environments (e.g., cacti in deserts).
Reproductive Structures
- Spore-producing plants: Thallophyta, Bryophyta, and Pteridophyta.
- Seed-producing plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
- Flowers are the reproductive organs in Angiosperms.
Economic Importance
- Food crops (wheat, rice), medicinal plants, timber, and ornamental plants.
- Source of industrial raw materials like cotton and jute.
Let’s practice!

