The Hierarchy Of Classification-Groups
Key Notes:
Definition of Biological Classification:
- Biological classification is the process of grouping organisms based on their similarities, differences, and evolutionary relationships.
Purpose of Classification:
- To organize vast biodiversity into manageable groups.
- To make the study of organisms easier and systematic.
- To understand evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomic Hierarchy:
- The hierarchy of classification groups is a series of ranks or levels in which organisms are classified.
- These levels range from the most general to the most specific.
Major Taxonomic Categories (Ranked from General to Specific):
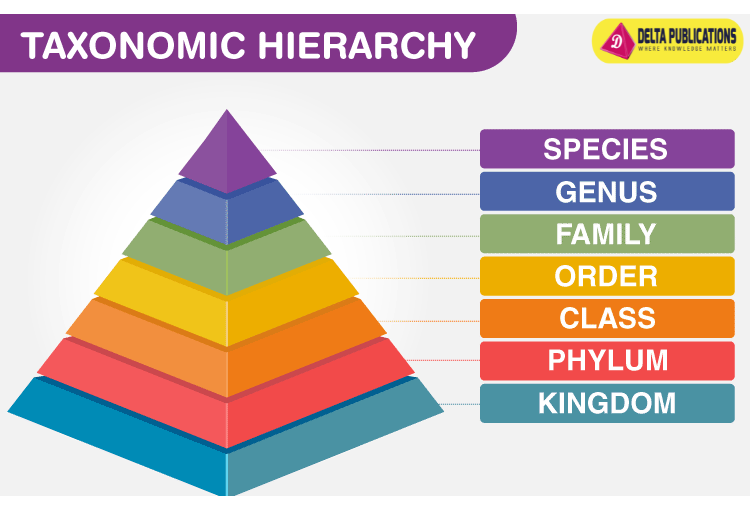
Kingdom:
- The highest and most general level of classification.
- Examples: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Monera.
Phylum (for animals) / Division (for plants):
- Groups organisms with a major body plan or structural similarity.
Class:
- A subset of a phylum; groups organisms with more specific common traits.
- Example: Mammalia (class of animals with hair and mammary glands).
Order:
- Groups closely related families.
- Example: Carnivora (includes dogs, cats, etc.).
Family:
- A group of related genera.
- Example: Felidae (family of cats).
Genus:
- Groups species that are structurally similar.
- Example: Panthera (includes lions, tigers, etc.).
Species:
- The most specific level; represents individuals capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
- Example: Homo sapiens (humans).
Mnemonic for Taxonomic Hierarchy:
- “King Philip Came Over For Great Soup” to remember the order: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Binomial Nomenclature:
- Developed by Carolus Linnaeus.
- Each organism is given a two-part scientific name: Genus and Species (e.g., Homo sapiens).
Importance of Taxonomic Hierarchy:
- Helps in the universal identification of organisms.
- Provides insight into evolutionary history and relationships.
- Avoids confusion caused by local names.
Examples of Classification:
- Humans:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Family: Hominidae
- Genus: Homo
- Species: Homo sapiens
- Mango tree (Mangifera indica):
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Division: Angiospermae
- Class: Dicotyledonae
- Order: Sapindales
- Family: Anacardiaceae
- Genus: Mangifera
- Species: indica
Challenges in Classification:
- Organisms with overlapping traits can complicate classification.
- Evolutionary changes may lead to reclassification.
Significance in Biology:
- Provides a framework for comparing organisms.
- Facilitates global scientific communication by standardizing names and categories.
Let’s practice!

