Classification And Evolution
Key Notes:
Introduction to Classification and Evolution
- Classification is the process of grouping organisms based on similarities and differences.
- Evolution refers to the gradual change in organisms over time, resulting in the diversity of life on Earth.
Importance of Classification
- Simplifies the study of a vast variety of organisms.
- Helps understand the relationships between different organisms.
- Provides insight into evolutionary connections.
Basis of Classification
- Homologous Structures: Similar structures in different organisms indicating a common ancestor (e.g., forelimbs of a frog and a bird).
- Analogous Structures: Structures with similar functions but different origins (e.g., wings of birds and insects).
- Embryological Evidence: Similar embryonic development patterns suggest common ancestry.
- Molecular Evidence: Similarities in DNA and protein structures.
Hierarchy of Classification
- Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species.
- Species is the most specific classification, grouping organisms capable of interbreeding.
Evolution and Natural Selection
- Proposed by Charles Darwin in his book On the Origin of Species.
- Evolution occurs through natural selection, where organisms better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce.
Fossil Evidence for Evolution
- Fossils are remains of ancient organisms preserved in rocks.
- They show a sequence of gradual changes leading to the development of modern organisms.
- Example: Fossil records of horses, showing a gradual increase in size and changes in foot structure.
Genetics and Evolution
- Variation in genetic material leads to evolution.
- Mutations, genetic drift, and recombination contribute to genetic diversity.
- Speciation: The formation of new species through evolution.
Human Evolution
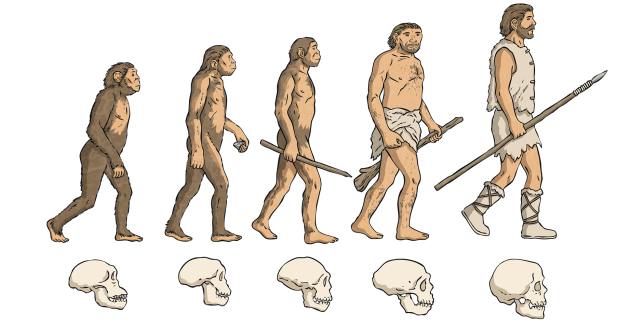
- Humans evolved from primates through a series of evolutionary changes.
- Evidence includes fossil findings like Australopithecus, Homo habilis, and Homo sapiens.
- Evolution is characterized by increased brain size, bipedalism, and tool-making abilities.
Applications of Classification and Evolution
- Helps in understanding the biodiversity and conservation of species.
- Plays a role in medical research and agriculture (e.g., pest-resistant crops).
Conclusion
- Classification and evolution are interconnected fields that explain the diversity of life.
- They highlight the unity and continuity of life forms through common ancestry.
Let’s practice!

