Animal Tissues
animal tissues by Delta publications
Key Notes:
Animal Tissues
- Definition: Tissues are groups of similar cells working together to perform a specific function in an organism.

- Types of Animal Tissues:
- Epithelial Tissue: Covers body surfaces and lines cavities, organs, and glands.
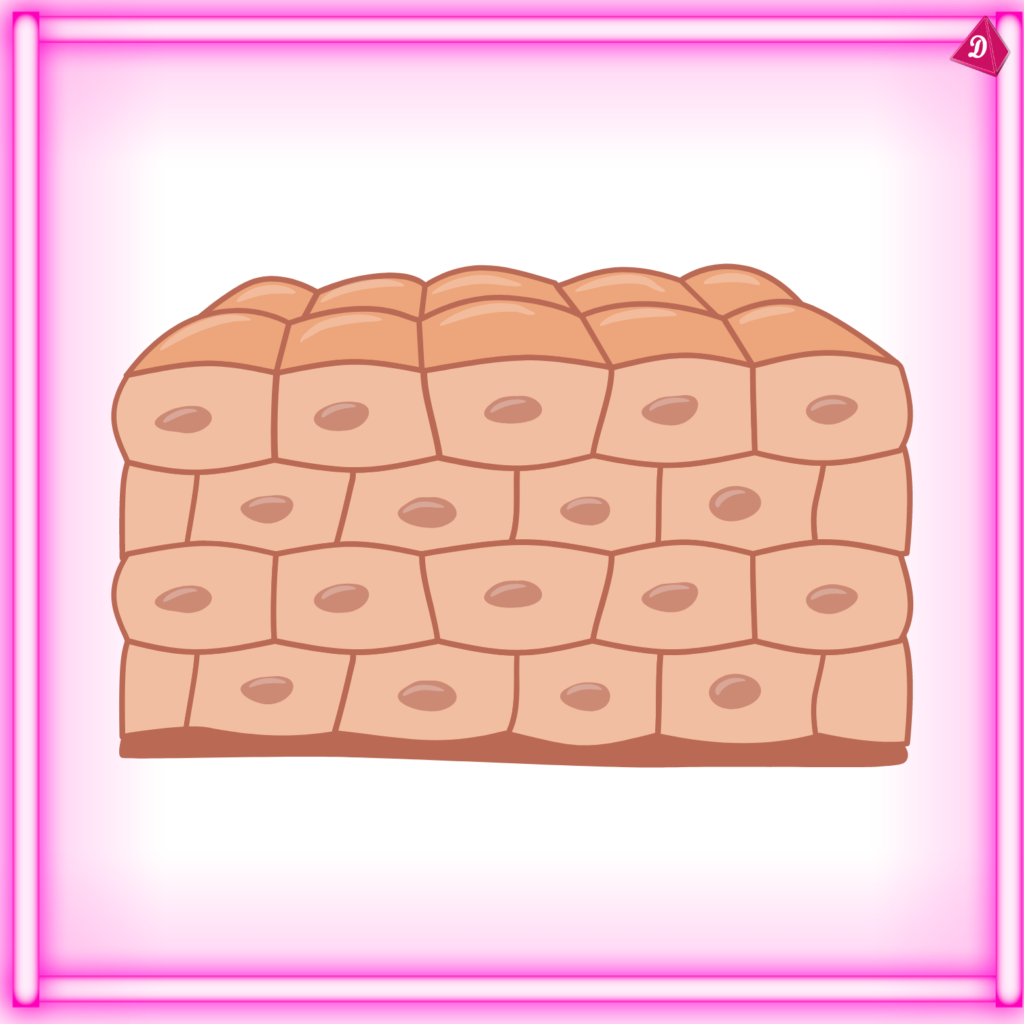
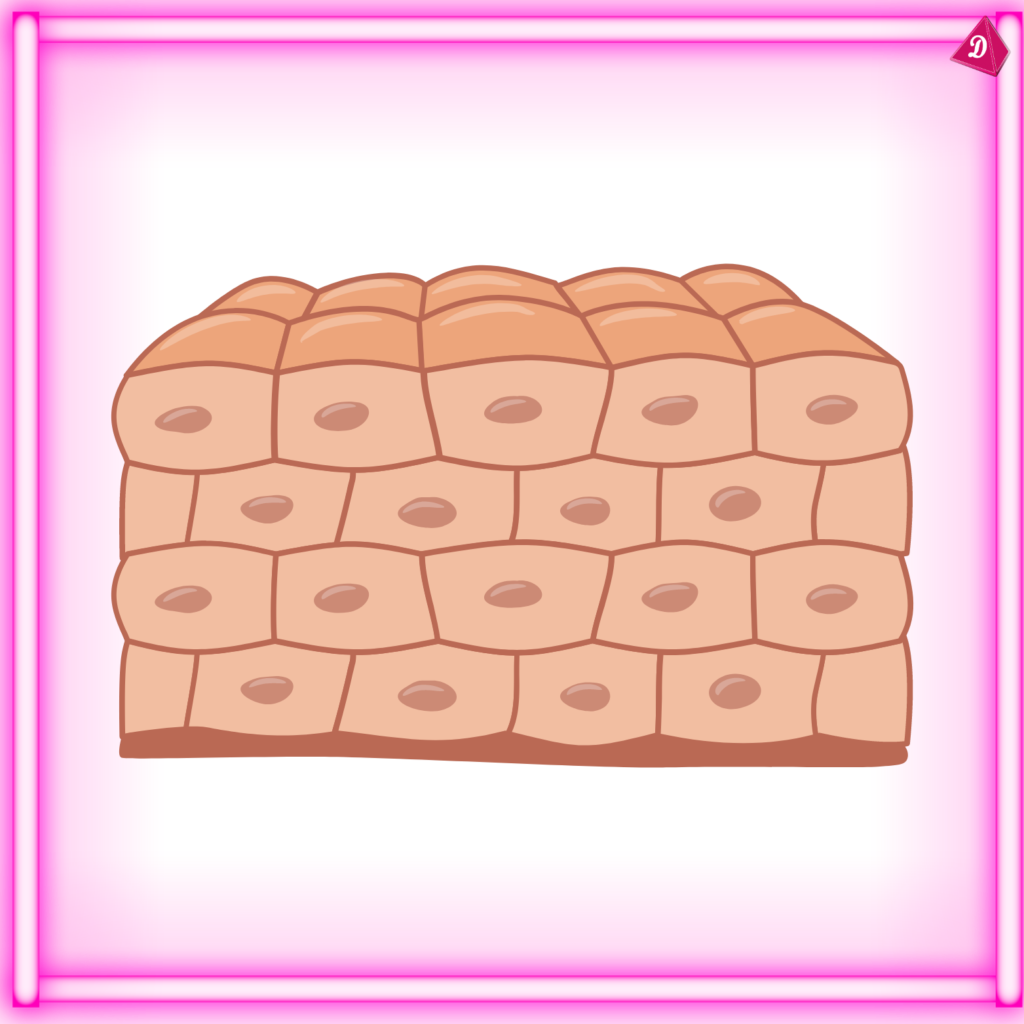
- Connective Tissue: Provides support and connects different tissues and organs.
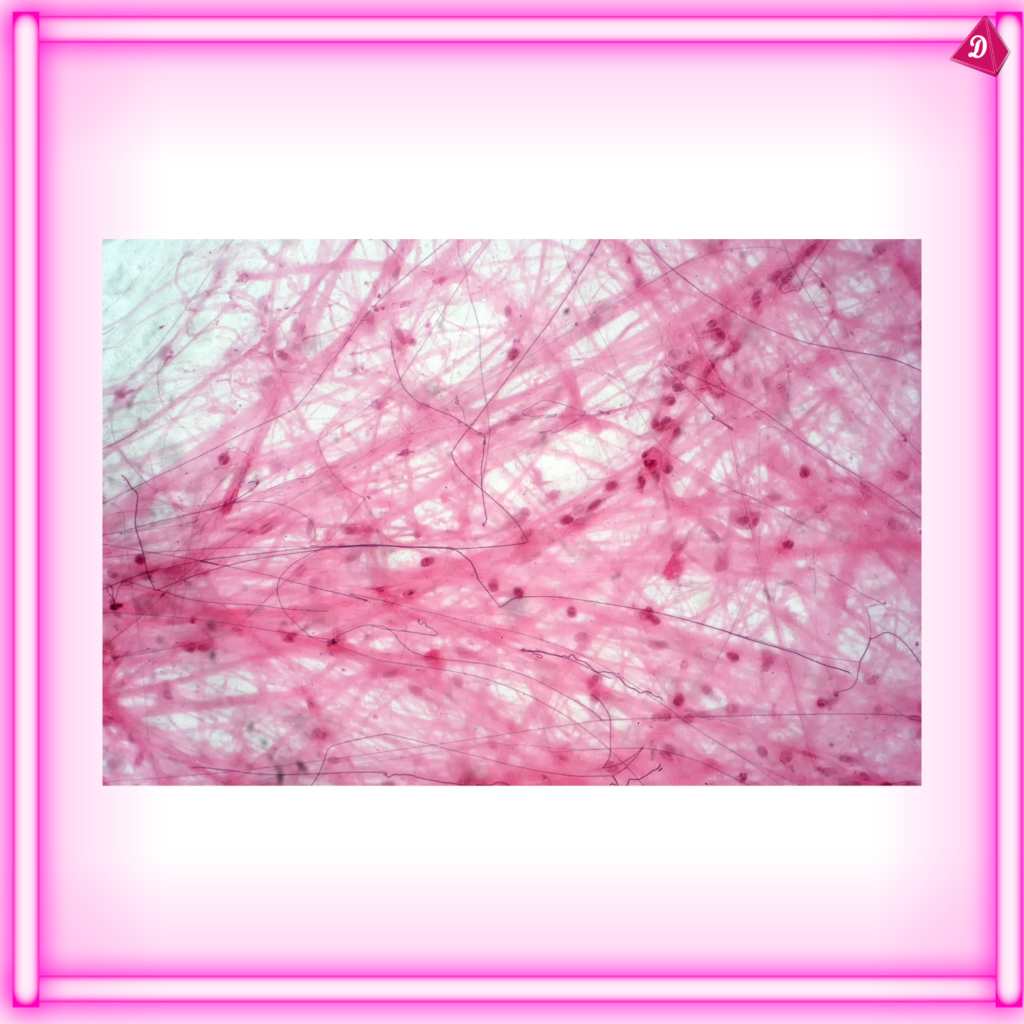
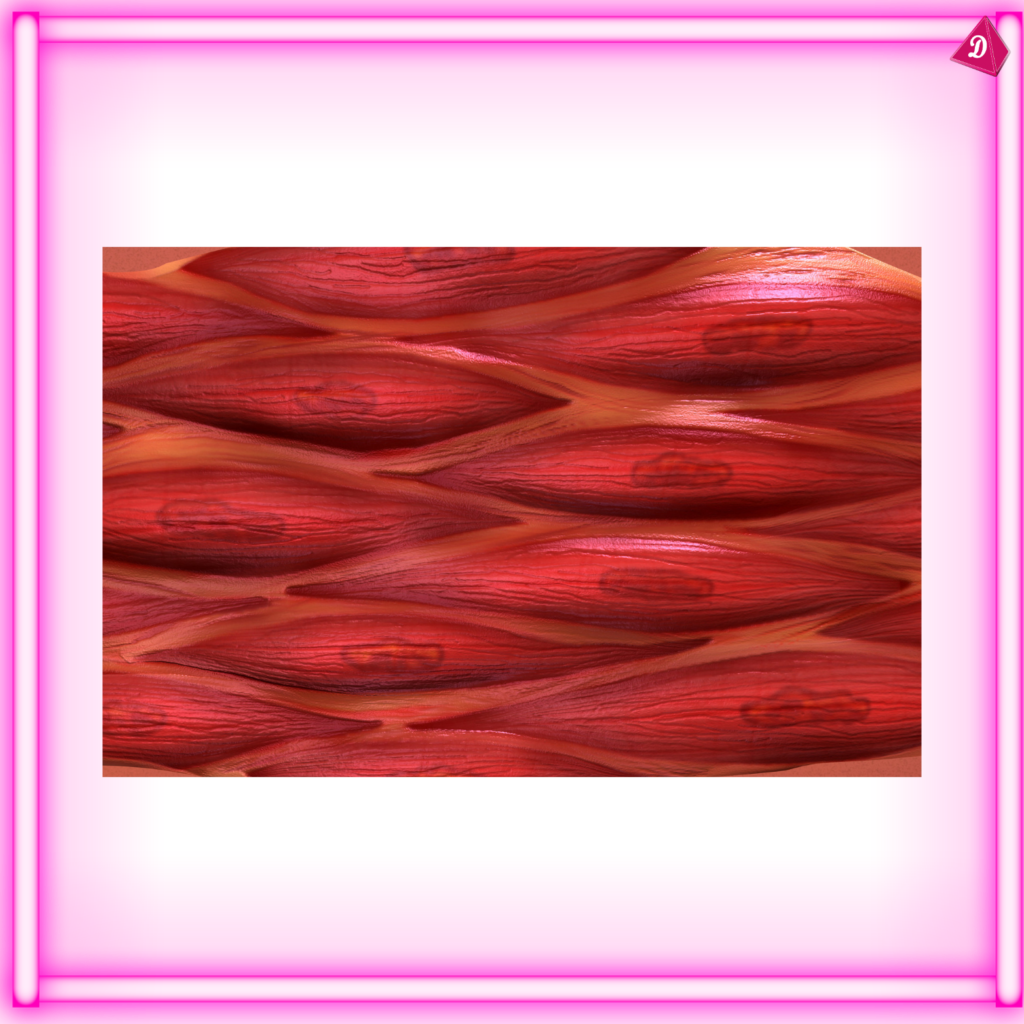
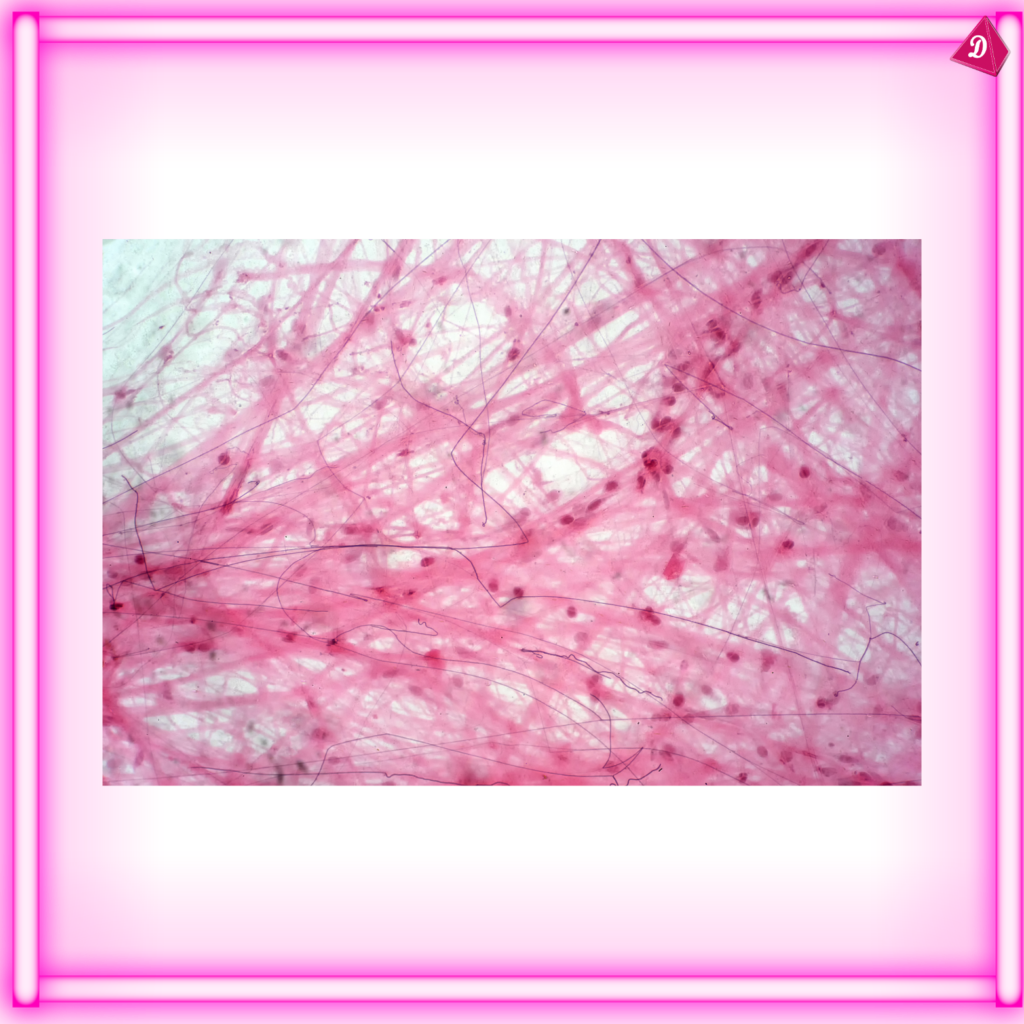
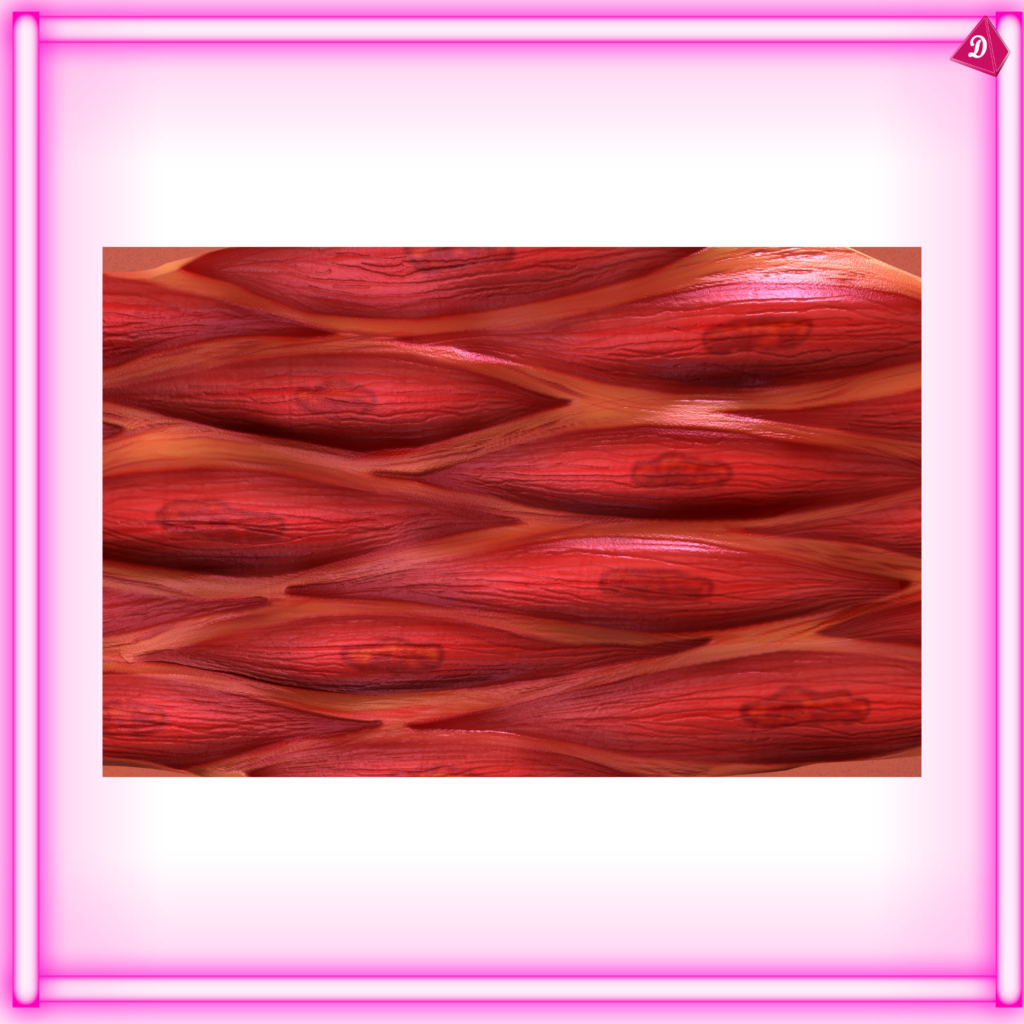
- Muscle Tissue: Responsible for movement and locomotion.

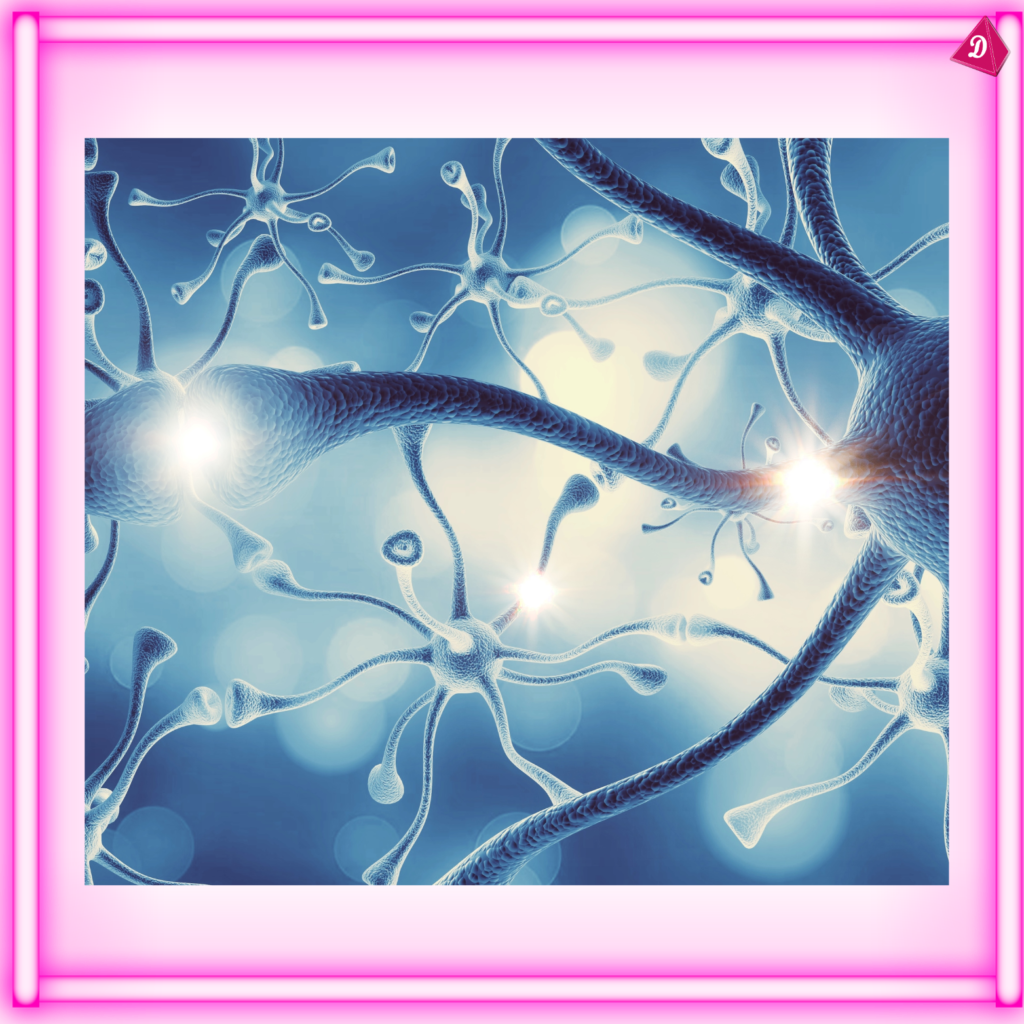
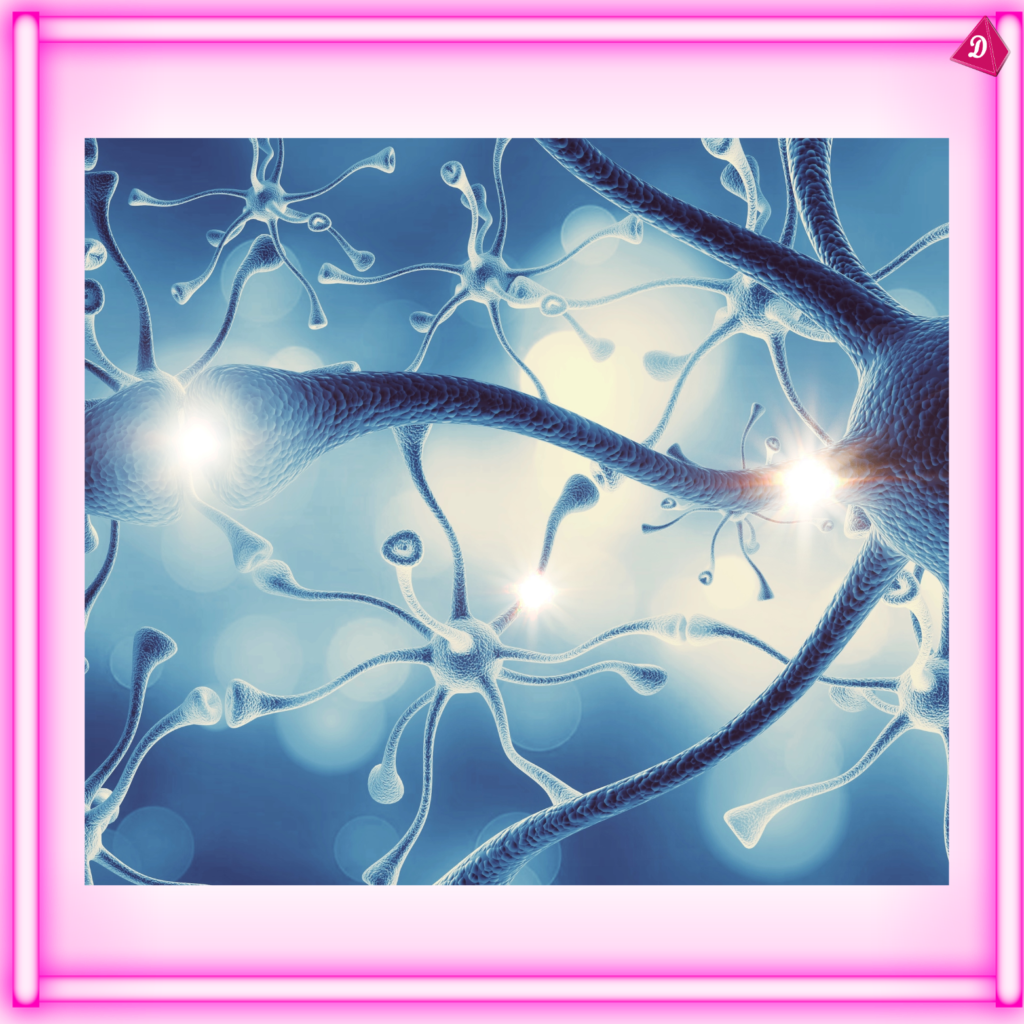
- Nervous Tissue: Transmits and receives nerve impulses, enabling coordination and control.

Epithelial Tissue:
- Found: Skin, lining of digestive tract, glands.
- Functions: Protection, absorption, secretion, and sensory reception.
- Types: Squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and transitional epithelium.
Connective Tissue:
- Found: Bone, cartilage, adipose tissue, blood.
- Functions: Support, protection, binding of organs, storage of fat, transport of substances.
- Types: Loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, cartilage, bone, blood.
Muscle Tissue:
- Found: Muscles attached to bones (skeletal), walls of hollow organs (smooth), heart (cardiac).
- Functions: Movement, posture, heat production.
- Types: Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle.

Nervous Tissue:
- Found: Brain, spinal cord, nerves.
- Functions: Transmission of nerve impulses, coordination, regulation of body functions.
- Types: Neurons (nerve cells) and neuroglia (supporting cells).

Organization and Functionality:
- Tissues organize into organs, and organs into organ systems, each contributing to overall organism function.
- Specialization of tissues allows for efficient performance of specific tasks essential for life.
Importance in Physiology:
- Understanding tissue structure and function aids in diagnosing and treating diseases.
- Provides insights into evolutionary adaptations and diversity among animal species.
Let’s practice!

