Isotopes
Key Notes:
Definition of Isotopes:
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
- This means isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Example of Isotopes:
- The most common example is Carbon:
- Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
- Carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons.
- Carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
- Despite having different mass numbers, all three isotopes of carbon behave chemically the same.
Atomic Number and Mass Number:
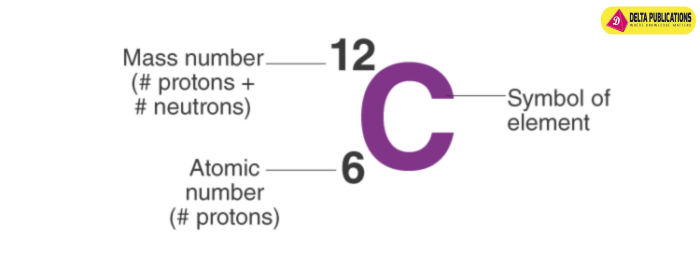
- Atomic number (Z) represents the number of protons in the nucleus and remains the same for isotopes of an element.
- Mass number (A) is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and varies among isotopes.
Representation of Isotopes:
- Isotopes are denoted using the element symbol followed by the mass number. For example, Carbon-12 (12C)
Physical vs. Chemical Properties:
- Isotopes of an element have identical chemical properties because they have the same electron configuration.
- They may have different physical properties like density, melting point, and stability due to differences in mass.
Radioactive Isotopes:
- Some isotopes are radioactive, meaning they decay over time and emit radiation. These are called radioisotopes.
- Example: Uranium-238 is a radioactive isotope used in nuclear reactors, while Carbon-14 is used in carbon dating to determine the age of fossils.
Applications of Isotopes:
- Medical: Radioisotopes like Cobalt-60 are used in cancer treatment and diagnostic imaging.
- Agriculture: Isotopes are used in tracing nutrient uptake in plants.
- Archaeology: Carbon-14 dating helps determine the age of ancient artifacts.
Stable vs. Unstable Isotopes:
- Stable isotopes do not change over time and do not emit radiation.
- Unstable isotopes (radioisotopes) undergo radioactive decay and can transform into other elements.
Isotopes in Nature:
- Elements in nature often exist as mixtures of their isotopes. For example, chlorine is a mix of Chlorine-35 and Chlorine-37.
- The average atomic mass of an element on the periodic table is a weighted average of its naturally occurring isotopes.
Importance of Isotopes:
- Isotopes play a crucial role in scientific research, medicine, environmental studies, and understanding the history of Earth and space.
Let’s practice!

