Molecular Mass And Mole Concept
Key notes :
Molecular Mass:
- Definition: Molecular mass is the mass of one molecule of a substance, calculated by adding the atomic masses of the atoms in the molecule.
- Unit: It is expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or g/mol.
- Example: The molecular mass of water (H₂O) is:
Molecular mass of H₂O = (2×1) + (1×16) = 18 amu
- Importance: It helps in calculating the amount of substance needed for reactions and determining the number of molecules.
Mole Concept:
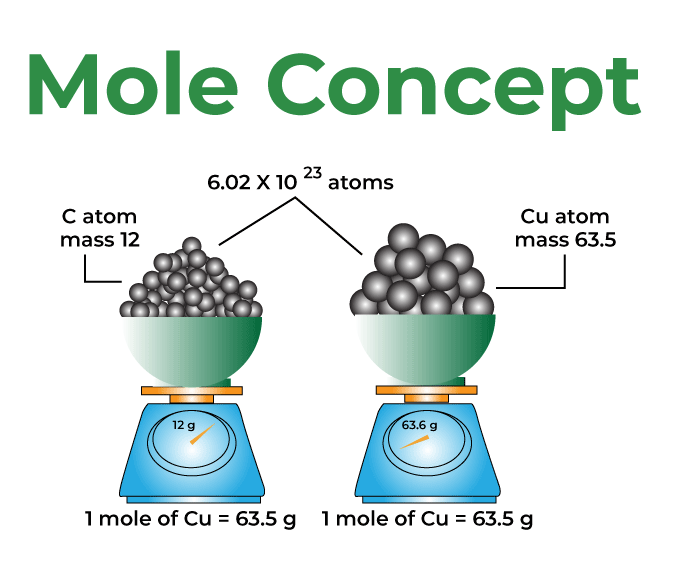
- Definition: A mole is a quantity used to count particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). One mole of any substance contains 6.022 × 10²³ particles (Avogadro’s number).
- Unit: Moles are expressed in mol.
- Formula:
Number of moles = Mass of substance (in grams) / Molar mass (g/mol)
- Example: If 18 grams of water (H₂O) is taken, the number of moles of water is:
Moles of H₂O = 18 g / 18 g / mol = 1 mole
Molar Mass:
- Definition: The molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, usually in units of grams per mole (g/mol).
- Relationship with Molecular Mass: Molar mass (g/mol) is numerically equal to molecular mass (amu), but the unit is grams per mole instead of atomic mass units.
- Example: For water (H₂O), the molecular mass is 18 amu, and the molar mass is 18 g/mol.
Avogadro’s Number:
- Definition: Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 10²³) is the number of particles in one mole of a substance.
- Example: One mole of carbon atoms contains 6.022 × 10²³ carbon atoms.
Mole and Chemical Reactions:
- Stoichiometry: The mole concept is essential in stoichiometry to calculate the amount of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- Balanced Equation: The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent the number of moles of each reactant and product involved.
Conversions:
- From grams to moles: Use the formula:
Moles = Mass (g) / Molar mass (g/mol)
- From moles to molecules: Use Avogadro’s number:
Number of molecules = Moles × (6.022 × 1023)
Application in Chemistry:
- Empirical Formula: The mole concept helps determine the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound.
- Molecular Formula: The actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule, determined using moles.
Summary:
- The mole concept links the atomic and macroscopic worlds.
- Molecular mass is the mass of a molecule, and molar mass is the mass of one mole of molecules.
- The mole is a convenient way to express quantities of substances involved in chemical reactions.
Let’s practice!

