Carbon And Oxygen Cycle
key notes :
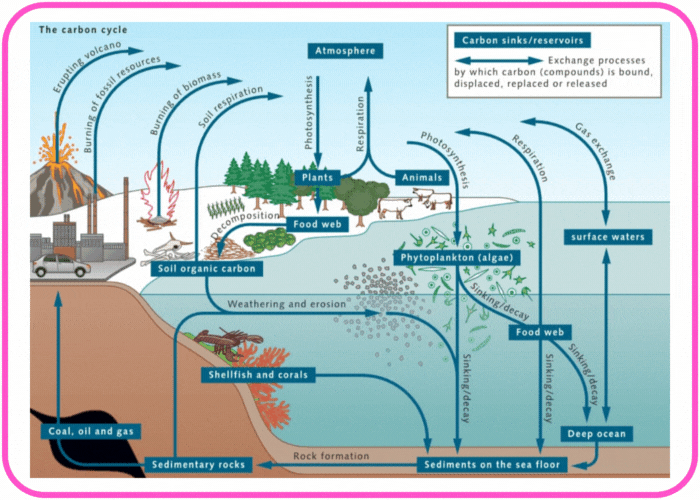
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves through the Earth’s ecosystems, atmosphere, and geosphere, ensuring the continuous availability of this vital element for life.
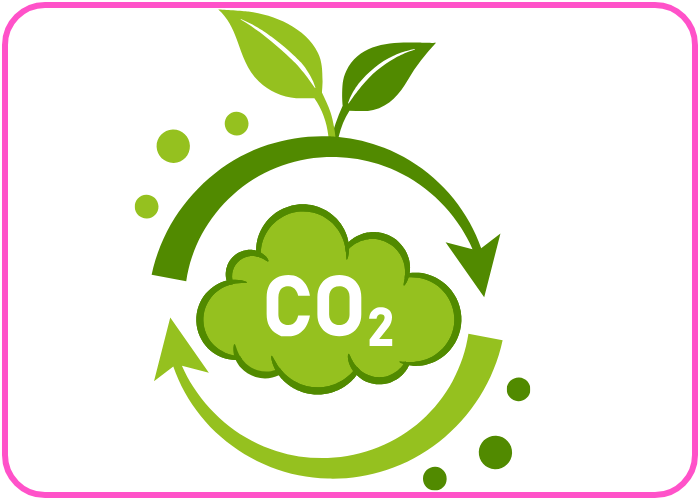

Key Processes in the Carbon Cycle
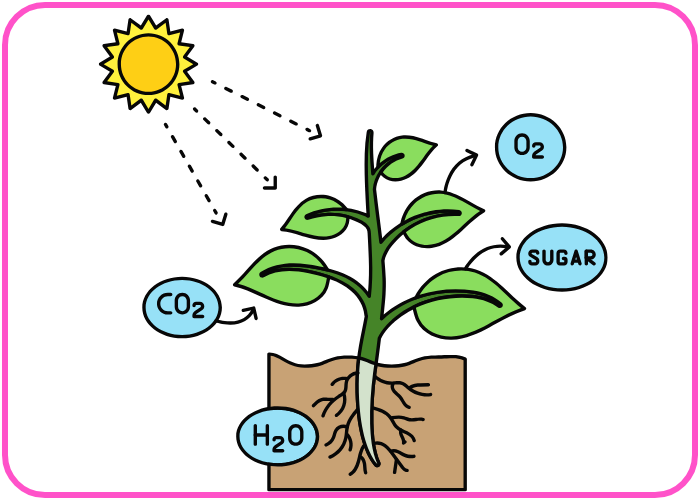
- Photosynthesis:
- Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere and use it to produce glucose and oxygen through photosynthesis.
- This process stores carbon in plant tissues.
- Respiration:
- Plants, animals, and microorganisms release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere by breaking down glucose during respiration.
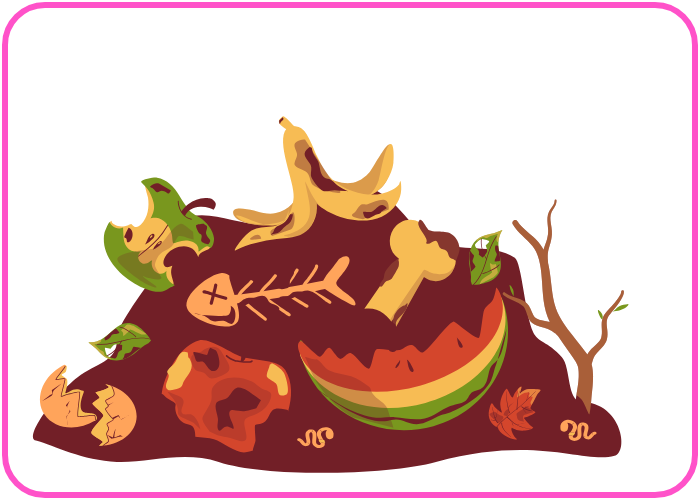
- Decomposition:
- Dead plants and animals are broken down by decomposers (bacteria and fungi), releasing carbon stored in their bodies back into the soil and atmosphere.

- Combustion:
- The burning of fossil fuels and biomass releases stored carbon as carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
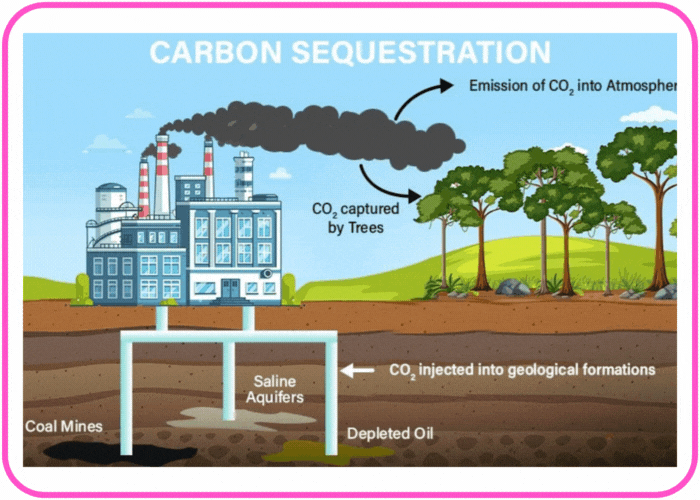
- Carbon Sequestration:
- Some carbon is stored long-term in the form of fossil fuels, limestone, or organic matter in the soil.
- Ocean Absorption:
- Oceans act as carbon sinks by absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere. Marine organisms use this carbon to build shells and skeletons, which eventually form limestone.
Importance of the Carbon Cycle
- Maintains a balance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Supports the production of energy and nutrients for living organisms.
- Regulates Earth’s temperature by controlling greenhouse gas levels.
Oxygen Cycle
The oxygen cycle describes the movement of oxygen within the atmosphere, biosphere, and lithosphere, ensuring the availability of this essential element for respiration and other life processes.
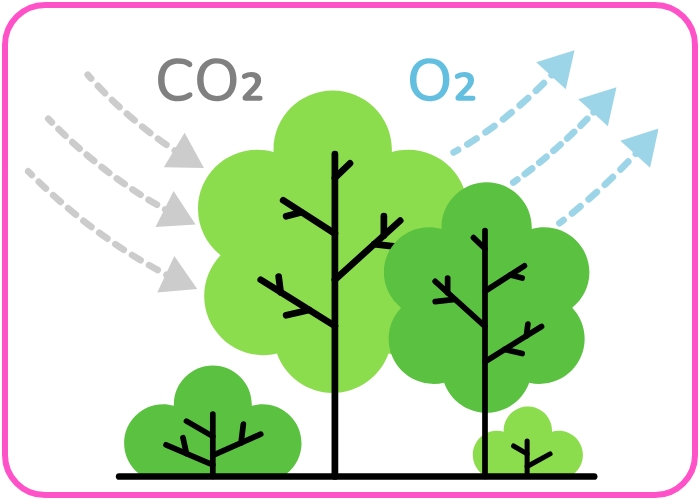
Key Processes in the Oxygen Cycle
- Photosynthesis:
- Plants release oxygen as a byproduct while converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
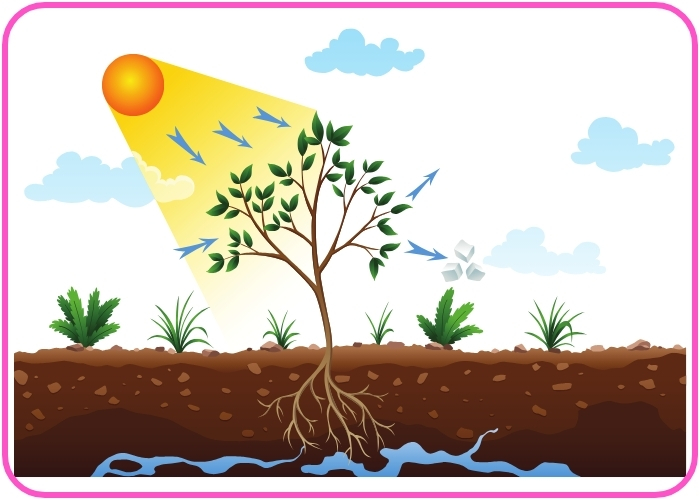

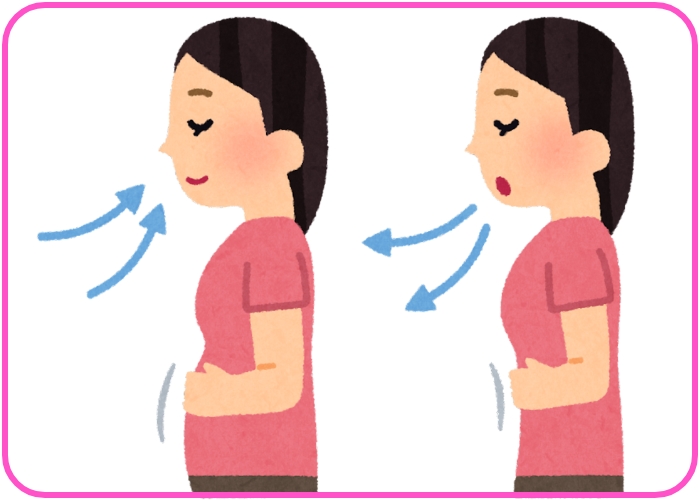
- Respiration:
- Oxygen is used by plants, animals, and microorganisms during respiration to produce energy, releasing carbon dioxide in the process.
- Decomposition:
- Decomposers use oxygen to break down organic matter, releasing nutrients and carbon dioxide.

- Ozone Formation and Breakdown:
- In the upper atmosphere, oxygen forms ozone (O₃), which protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Ozone is also naturally broken down into oxygen.
- Weathering of Rocks:
- Oxygen reacts with minerals in rocks during weathering, forming oxides and contributing to soil formation.
Importance of the Oxygen Cycle
- Supports life through respiration.

- Plays a vital role in maintaining Earth’s atmospheric composition.

- Regulates environmental processes like decomposition and weathering.

Interconnection of Carbon and Oxygen Cycles
- The two cycles are closely linked through photosynthesis and respiration.
- Plants use carbon dioxide and release oxygen, while animals use oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
- Both cycles play a crucial role in maintaining Earth’s ecological balance and supporting life.
Let’s practice!

