Different Types Of Animal Behaviour
key notes :
- Instinctive Behavior:
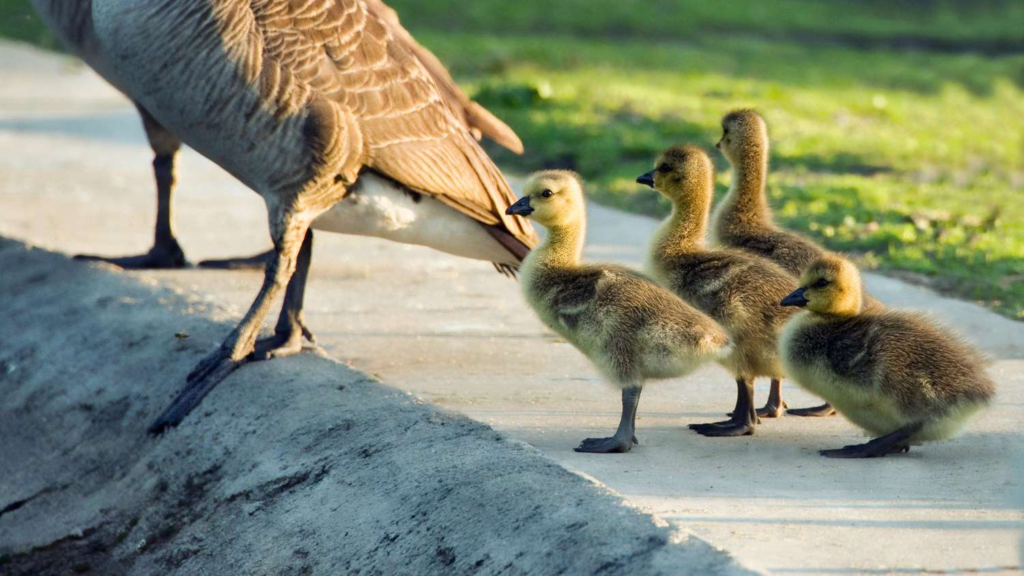

- Instincts are innate behaviors that animals are born with.
- They are often automatic and do not require learning.
- Examples include birds building nests or a spider spinning a web.
- Learned Behavior:

- Some behaviors are acquired through experience and learning.
- Animals can learn from their environment or from other animals.
- Examples include dogs learning commands, and birds learning to sing specific songs.
- Social Behavior:
- Many animals are social and live in groups or communities.
- Social behavior includes activities like communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution.
- Examples include wolves hunting in packs and bees working together in a hive.
- Communication:
- Animals use various forms of communication to convey information.
- This can include vocalizations, body language, scent marking, and visual displays.
- Communication is crucial for mating, warning of danger, and establishing social hierarchies.
- Territorial Behavior:
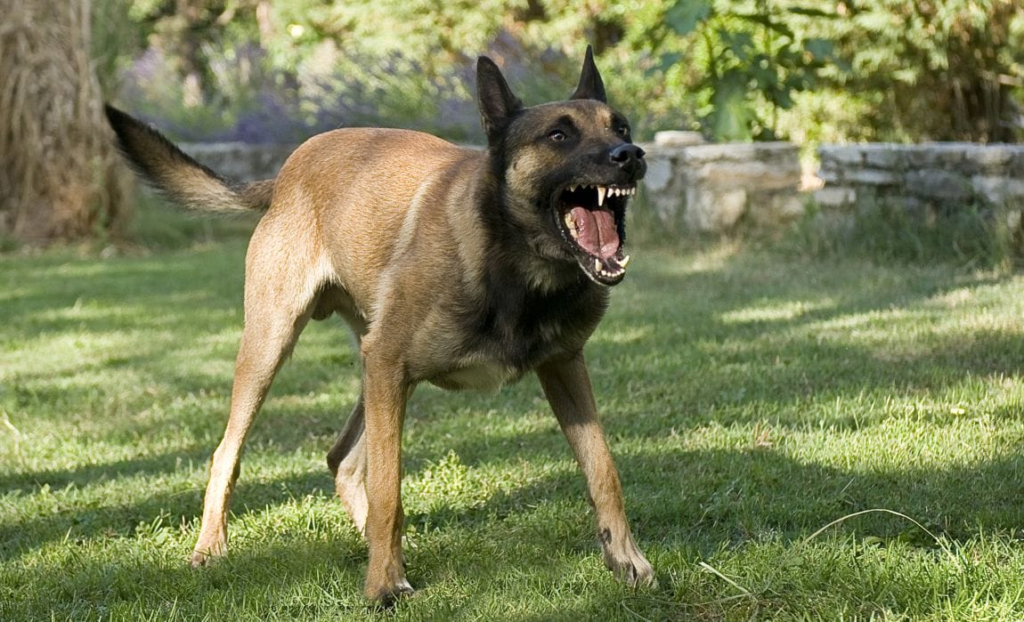

- Some animals defend and mark territories to secure resources and mates.
- Territorial displays and aggression can deter intruders.
- Examples include a lion marking its territory with urine or a dog guarding its home.
- Reproductive Behavior:
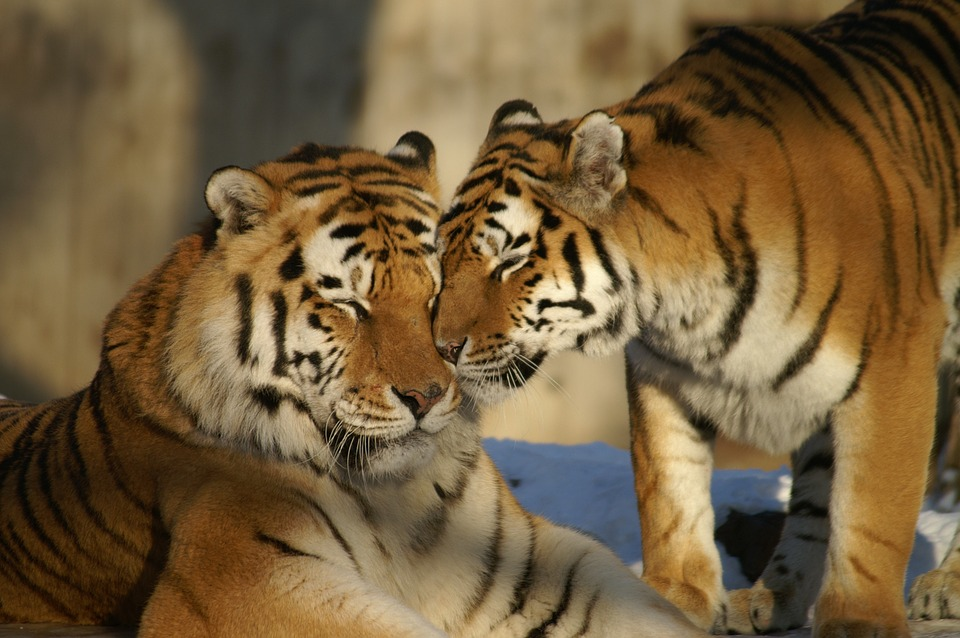

- Animals have specific behaviors related to reproduction.
- These can include courtship rituals, mating displays, and parenting.
- Examples include the intricate courtship dance of peacocks and the care provided by mother birds to their chicks.
- Migration:
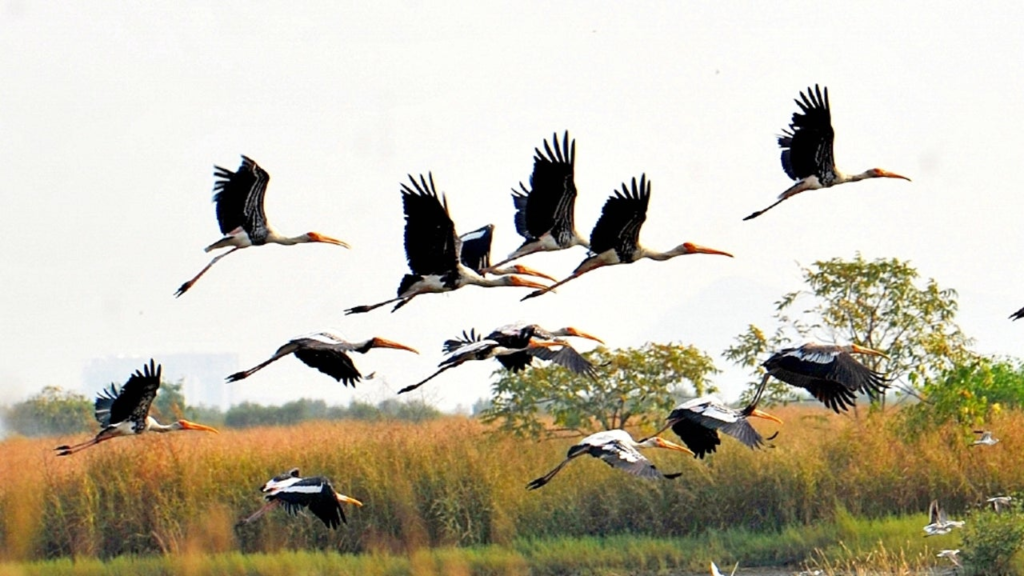

- Many animals undertake long-distance seasonal migrations.
- Migration helps them find food, escape harsh conditions, or reproduce.
- Examples include the annual migration of monarch butterflies and the journeys of whales.
- Hibernation and Estivation:
- Some animals enter states of dormancy to conserve energy during unfavorable conditions.
- Hibernation occurs in winter, while estivation occurs in hot, dry conditions.
- Examples include bears hibernating in the winter and certain frogs estivating during droughts.
- Aggressive Behavior:
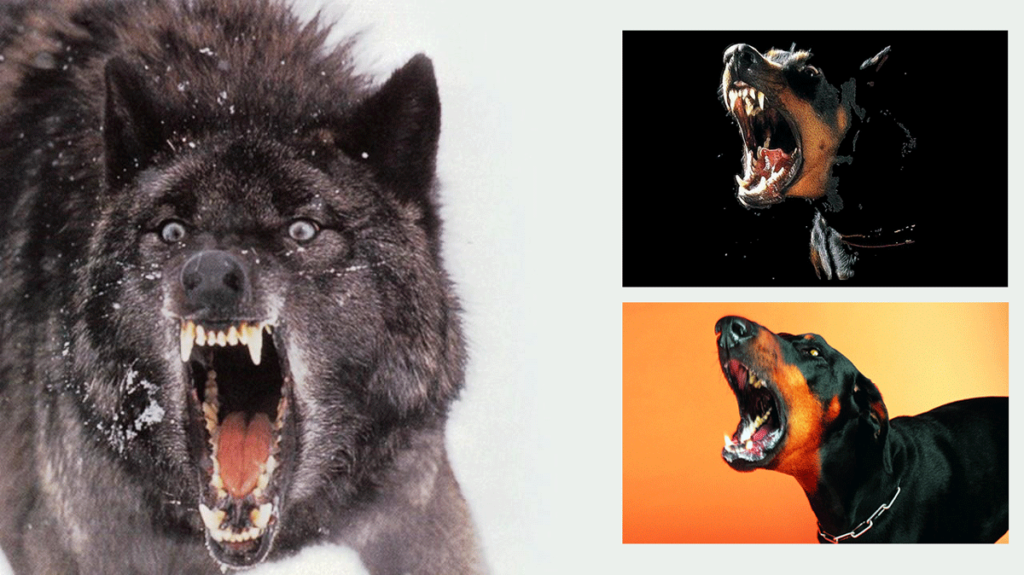

- Animals may display aggression to establish dominance, defend territory, or secure resources.
- Aggression can vary from threats and displays to physical combat.
- Examples include fights between male deer during the mating season and conflicts among rival wolves.
- Altruistic Behavior:
- Altruism is when animals perform actions that benefit others at a cost to themselves.
- This behavior is often seen in social animals where cooperation is essential.
- Examples include meerkats taking turns to act as sentinels to watch for predators and bees sacrificing themselves to protect the hive.
Let’s practice!

