What Are The Types Of Pure Substances?
What Are The Types Of Pure Substances? by Delta publications
Key Notes:
Definition of Pure Substances:
- Pure substances consist of only one type of particle (atoms or molecules).
- They have a uniform and definite composition throughout.
Types of Pure Substances:
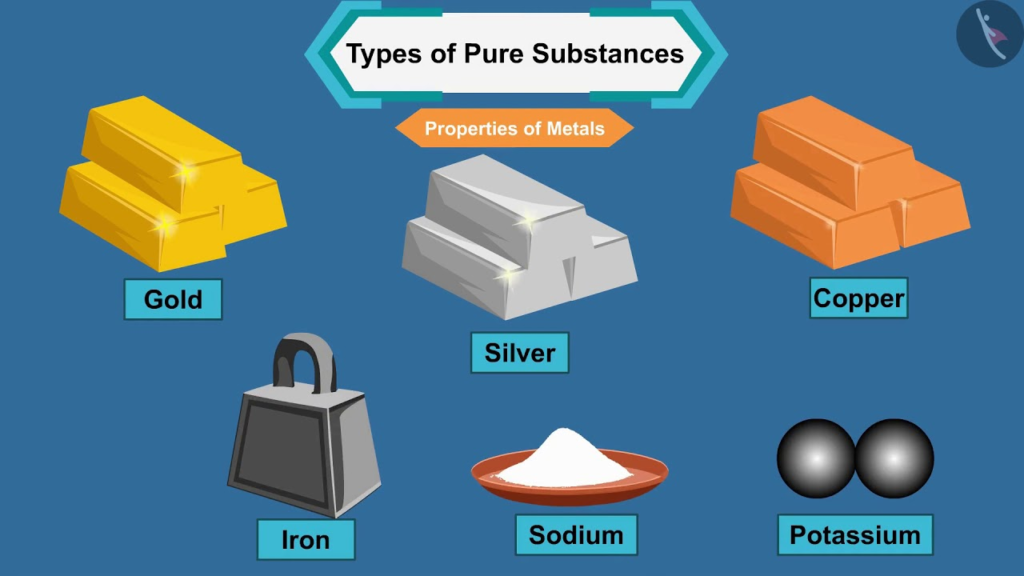
- Elements:
- Made up of only one type of atom.
- Cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
- Examples: Oxygen (O₂), Gold (Au), Hydrogen (H₂).
- Compounds:
- Formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
- Can be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
- Examples: Water (H₂O), Sodium Chloride (NaCl), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂).
Characteristics of Elements:
- Exist as metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
- Examples:
- Metals: Iron (Fe), Aluminum (Al).
- Non-Metals: Carbon (C), Sulfur (S).
- Metalloids: Boron (B), Silicon (Si).
Characteristics of Compounds:
- Have properties different from their constituent elements.
- Always combine in a fixed ratio by mass (Law of Definite Proportions).
- Examples:
- Water (H₂O): Made of hydrogen and oxygen, but different properties from both.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Combines carbon and oxygen in a 1:2 ratio.
Differences Between Elements and Compounds:
| Property | Elements | Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | One type of atom | Two or more types of atoms |
| Separation Methods | Cannot be broken down | Can be broken into elements |
| Examples | Oxygen (O₂), Copper (Cu) | Water (H₂O), Sodium Chloride (NaCl) |
Importance of Pure Substances:

- Used in scientific research for consistency.
- Essential in manufacturing, like making medicines and alloys.
Testing Purity:
- Pure substances have specific melting and boiling points.
- Impurities alter these properties.
Everyday Examples:
- Elements: Aluminum foil, oxygen gas.
- Compounds: Salt in food, sugar in drinks.
Let’s practice!

