Physical And Chemical Changes
physical and chemical changes by Delta publications
Key notes :
Definition
- Physical Change: A change in which no new substance is formed; only the physical properties (like shape, size, or state) change.
- Chemical Change: A change that results in the formation of one or more new substances with different properties.
Characteristics of Physical Changes

- Reversible in most cases (e.g., melting of ice, dissolving sugar in water).
- No change in the chemical composition of the substance.
- Energy changes are usually small.
- Examples: Boiling of water, breaking of glass, and stretching of rubber.
Characteristics of Chemical Changes
- Usually irreversible (e.g., burning of wood, rusting of iron).
- Involves a chemical reaction and formation of new substances.
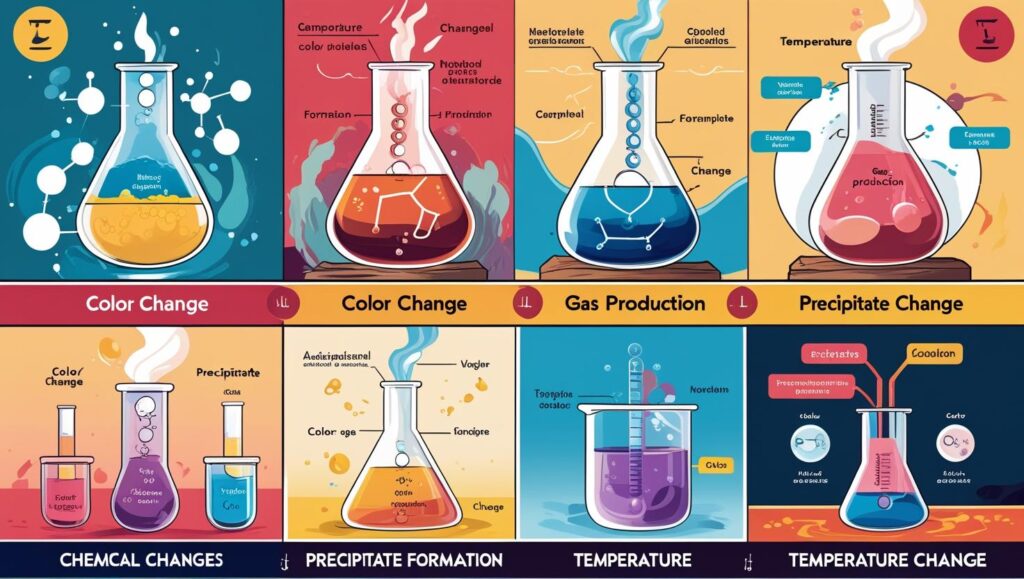
- Accompanied by changes like color, temperature, emission of gas, or formation of precipitate.
- Energy changes are significant (absorption or release of heat or light).
- Examples: Cooking food, photosynthesis, and combustion.
Indicators of a Chemical Change
- Change in color: Rusting of iron changes the surface color to reddish-brown.
- Change in temperature: Combustion releases heat.
- Formation of gas: Effervescence observed in vinegar reacting with baking soda.
- Formation of precipitate: Reaction between solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride forms a white precipitate of silver chloride.
Comparison Between Physical and Chemical Changes
| Aspect | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| Formation of New Substance | No | Yes |
| Reversibility | Mostly reversible | Mostly irreversible |
| Energy Change | Low | High |
| Examples | Melting of ice, cutting of paper | Burning of coal, souring of milk |
Real-life Applications
- Physical Changes: Freezing water for ice, evaporating water to purify it.
- Chemical Changes: Digestion of food, rust prevention, and fuel combustion.
Conservation of Mass
- Both physical and chemical changes obey the law of conservation of mass, meaning the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
Experiment Examples
- Physical change: Boiling water to steam.
- Chemical change: Adding vinegar to baking soda to observe gas release (CO₂ formation).
Common Misconceptions
- Melting of wax is a physical change, but burning of wax is a chemical change.
- Dissolving sugar in water is a physical change, as no new substance forms.
Let’s practice!

