Separation Of Components Of A Mixture
Separation Of Components Of A Mixture by Delta publications
Key notes :
Definition of Mixtures:
- Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically combined.
- Components of a mixture retain their individual properties.
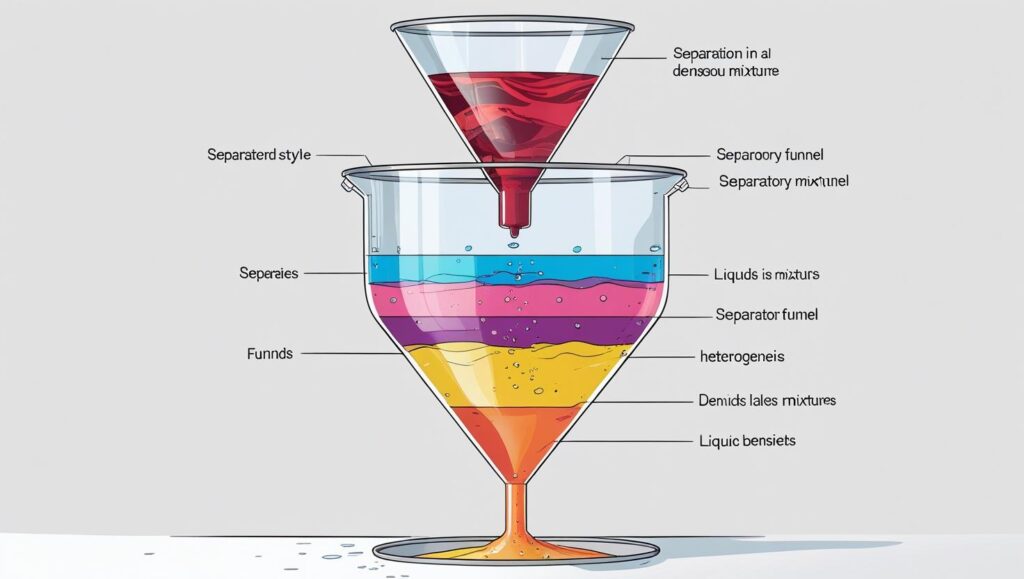
Types of Mixtures:
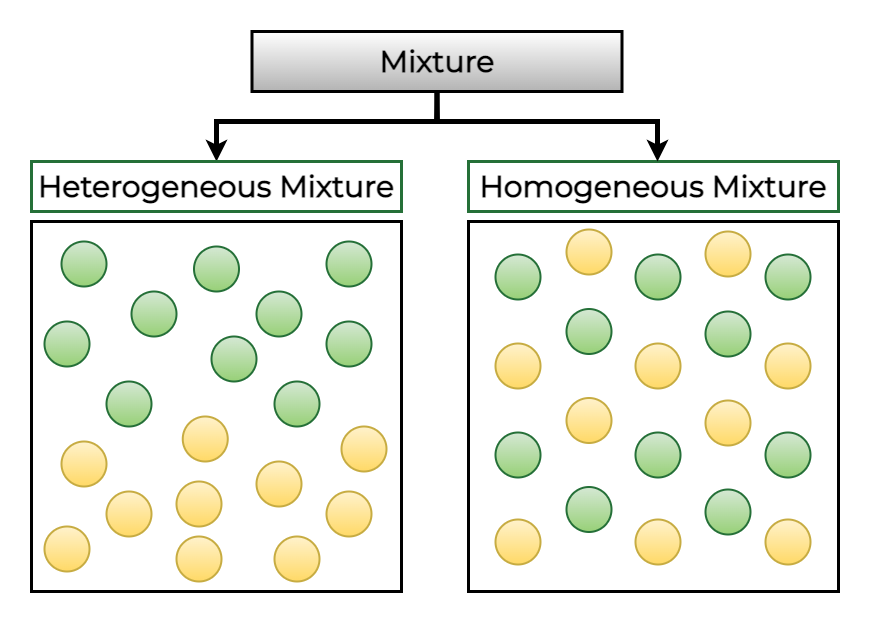
- Homogeneous Mixtures: Uniform composition throughout (e.g., saltwater).
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: Non-uniform composition (e.g., sand and water).
Need for Separation:
- To remove unwanted materials.
- To obtain pure substances for specific uses.
- To recover valuable components.
Principles of Separation:
- Based on differences in physical properties like particle size, solubility, boiling point, density, or magnetic properties.
Methods of Separation:
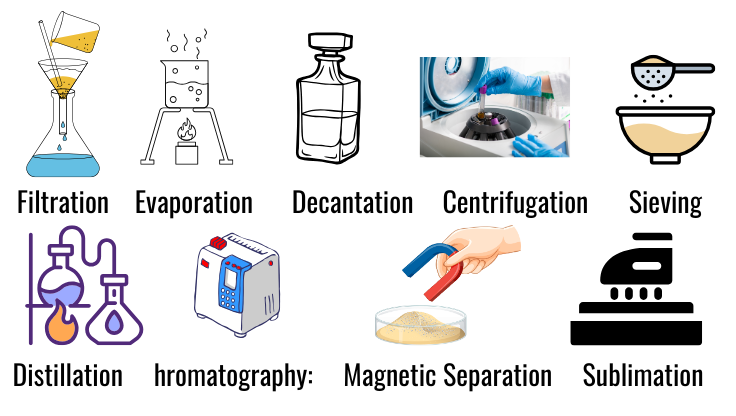

- Filtration:
- Used to separate insoluble solids from liquids (e.g., sand from water).
- Evaporation:
- Removes a liquid to leave behind a dissolved solid (e.g., salt from seawater).
- Decantation:
- Separates liquid from insoluble solids by pouring off the liquid (e.g., oil and water).
- Centrifugation:
- Uses centrifugal force to separate fine solids from liquids (e.g., separating cream from milk).
- Distillation:
- Separates liquids based on boiling points (e.g., separating alcohol from water).
- Chromatography:
- Separates mixtures based on different affinities for a stationary and mobile phase (e.g., inks or dyes).
- Magnetic Separation:
- Uses a magnet to separate magnetic materials from a mixture (e.g., iron from sulfur).
- Sublimation:
- Separates substances that sublime directly from solid to gas (e.g., iodine or camphor).
- Sieving:
- Separates particles of different sizes (e.g., flour and husk).
Examples of Mixtures:
- Sugar solution: Can be separated by evaporation.
- Muddy water: Can be separated by filtration and decantation.
- Iron filings and sulfur: Can be separated using a magnet.
Applications:
- Purification of water.
- Extraction of metals from ores.
- Separation of chemicals in the pharmaceutical industry.
Real-Life Importance:
- Ensures food and medicine purity.
- Aids in environmental conservation (e.g., wastewater treatment).
Practical Demonstrations:
- Show filtration using sand and water.
- Demonstrate evaporation with saltwater.
Lets’practice :

