What Is A Solution
What is a solution by Delta publications
Key Notes:
Definition of a Solution
- A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances.
- In a solution, one substance is dissolved in another, resulting in a single phase.
Components of a Solution
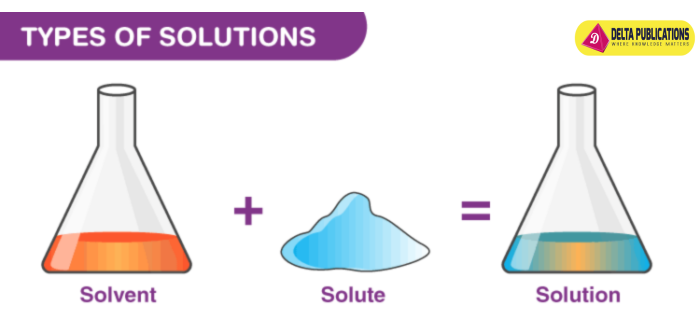
- Solvent: The substance that dissolves the solute. It is usually present in the largest amount (e.g., water in saltwater).
- Solute: The substance that is dissolved in the solvent (e.g., salt in saltwater).
Characteristics of Solutions
- Uniformity: Solutions have a uniform composition and appearance throughout.
- Particle Size: The particles of solute in a solution are at the molecular or ionic level, usually smaller than 1 nanometer.
- Transparency: Many solutions are clear and do not scatter light, although some may be colored.
Types of Solutions
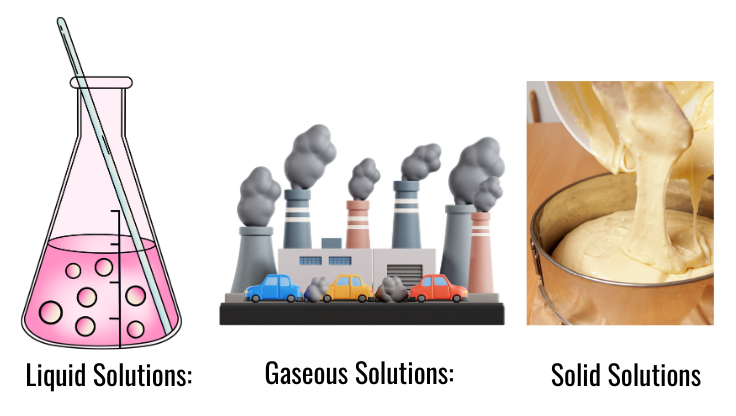

- Liquid Solutions: Most common; involves liquids (e.g., saltwater, sugar water).
- Gaseous Solutions: Involves gases (e.g., air is a mixture of gases).
- Solid Solutions: Involves solids (e.g., alloys like bronze, which is a mixture of copper and tin).
Properties of Solutions
- Concentration: Refers to the amount of solute present in a given amount of solvent or solution. It can be expressed in various ways, such as molarity or percentage.
- Saturation: A solution is saturated when it cannot dissolve any more solute at a given temperature and pressure.
- Solubility: Refers to the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of solvent at a given temperature.
Factors Affecting Solubility
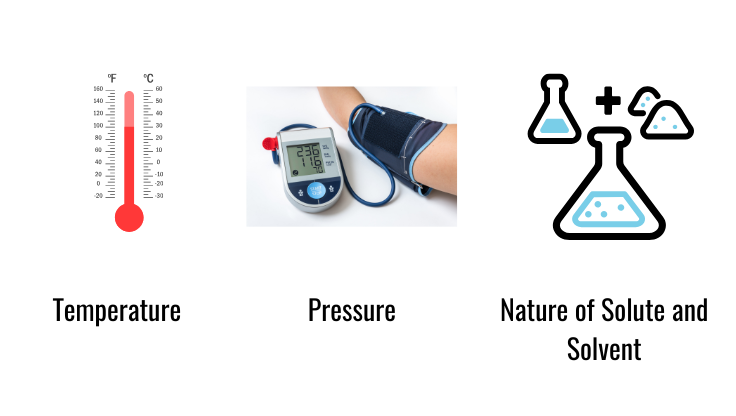
- Temperature: Generally, higher temperatures increase solubility for solids in liquids but can decrease it for gases.
- Pressure: Increased pressure generally increases the solubility of gases in liquids.
- Nature of Solute and Solvent: “Like dissolves like” principle; polar solvents dissolve polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes.
Applications of Solutions
- Solutions are essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry.
- Common examples include drinking solutions (e.g., lemonade), cleaning products (e.g., detergents), and pharmaceuticals (e.g., saline solutions).
Let’s practice!

