What Is A Mixture?
What is a mixture? by Delta publications
Key Notes:
Definition of Mixture:
- A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically combined.
- Each substance in a mixture retains its individual chemical properties.
Characteristics of Mixtures:

- The components can be separated by physical methods (e.g., filtration, distillation).
- No chemical change occurs when forming a mixture.
- The composition of a mixture is not fixed and can vary.
Types of Mixtures:

- Homogeneous Mixtures: The composition is uniform throughout (e.g., saltwater, air).
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: The composition is not uniform and components are visibly distinct (e.g., sand and iron filings).
Examples of Mixtures:
- Homogeneous: Sugar dissolved in water, vinegar.
- Heterogeneous: Oil and water, a bowl of cereal with milk.
Separation Techniques:
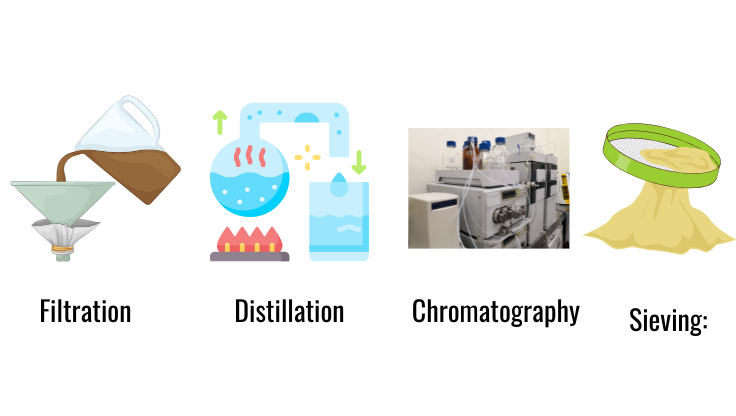
- Filtration: Separates solid particles from a liquid.
- Distillation: Separates components based on boiling points.
- Chromatography: Separates based on movement through a medium.
- Sieving: Separates particles of different sizes.
Importance of Mixtures in Daily Life:
- Used in food preparation (e.g., salad, juice).
- Industrial applications (e.g., alloys like steel).
- Medical uses (e.g., saline solution).
Comparison with Pure Substances:
- Pure Substances: Have a fixed composition and cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical methods.
- Mixtures: Have variable composition and can be separated physically.
Properties of Mixtures:

- Do not have a fixed melting or boiling point.
- Exhibit properties of their individual components.
Let’s practice!

