Nervous Cells
key notes :
Nervous Cells (Neurons):
- Introduction:
- Nervous cells, or neurons, are the fundamental building blocks of the nervous system.
- They play a crucial role in transmitting and processing information in our body.
- Structure of Neurons:
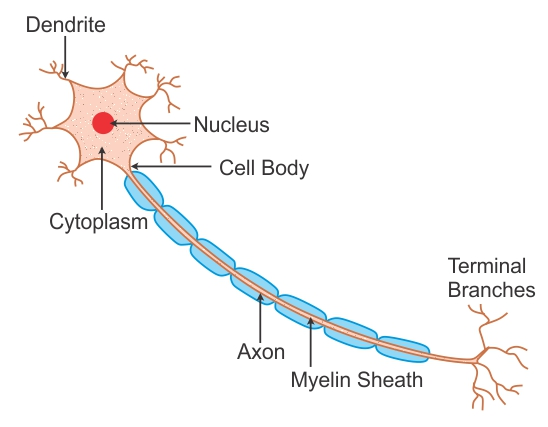
- Neurons have three main parts: cell body, dendrites, and axon.
- The cell body contains the nucleus and other essential organelles.
- Dendrites receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors.
- The axon is a long, slender projection that carries signals away from the cell body.
- Function of Neurons:
- Neurons transmit electrochemical signals called nerve impulses or action potentials.
- These impulses allow communication between different parts of the nervous system.
- Neurons enable us to think, perceive, move, and feel.
- Types of Neurons:
- Sensory Neurons: Transmit sensory information from sensory organs to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Motor Neurons: Carry signals from the CNS to muscles and glands, controlling movements and responses.
- Interneurons: Found within the CNS, they relay signals between sensory and motor neurons.
- Synapses:
- Neurons communicate at junctions called synapses.
- Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals across synapses.
- This process allows for information to be transferred from one neuron to another.
- Importance of Neurons:
- Neurons are essential for basic bodily functions, such as breathing and reflexes.
- They are also responsible for complex cognitive processes like thinking, learning, and memory.
- Protection of Neurons:
- Neurons are delicate cells and need protection.
- They are surrounded by a protective layer called the myelin sheath, which speeds up signal transmission.
- The skull and spine protect neurons in the brain and spinal cord.
- Neurological Disorders:
- Disorders related to neurons can have a significant impact on health.
- Examples include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- Conclusion:
- Nervous cells (neurons) are the basic units of the nervous system.
- They are responsible for transmitting and processing information that controls our body’s functions and behaviors.
Let’s practice!

