Cell Organelles
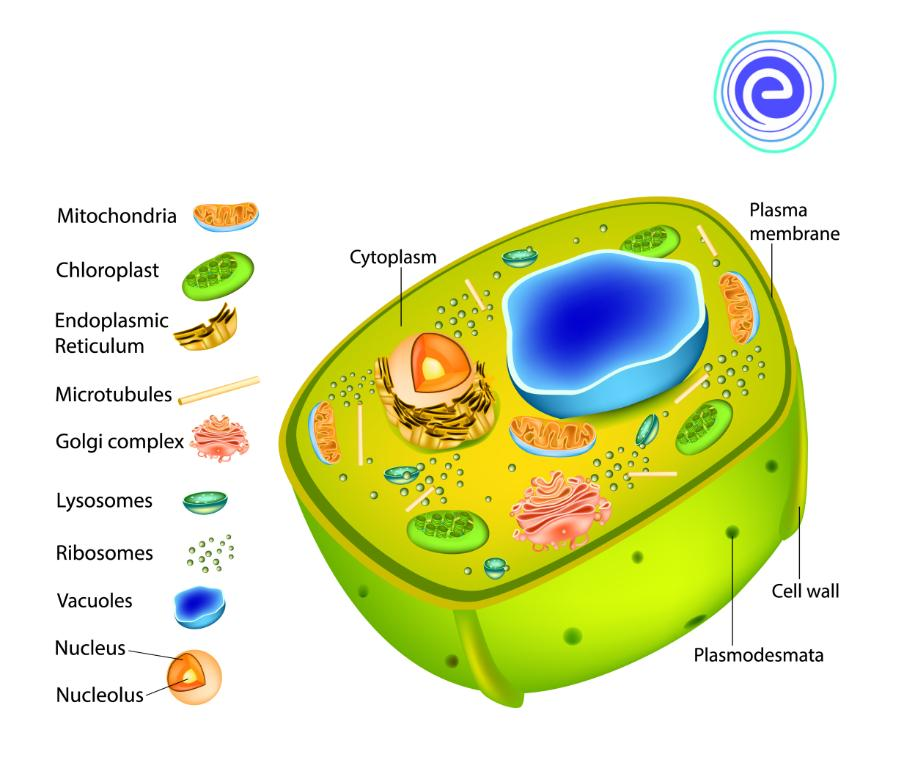
key notes :
Introduction:
- Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and they come in various types, each with specialized functions.
- Within cells, there are smaller structures called organelles, which have specific roles in maintaining cell function and supporting life processes.
1. Cell Membrane:
- The cell membrane is the outer boundary of the cell, also known as the plasma membrane.
- It controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell, ensuring a stable internal environment.
2. Nucleus:
- The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell.
- It contains genetic material (DNA) that carries instructions for cell functions and heredity.
3. Cytoplasm:
- Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell’s interior.
- It holds organelles in place and facilitates various cellular processes.
4. Mitochondria:
- Mitochondria are the “powerhouses” of the cell, where energy (ATP) is produced through cellular respiration.
5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
- The ER is a network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Rough ER has ribosomes and produces proteins, while smooth ER is involved in lipid metabolism.
6. Golgi Apparatus:
- The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cell.
7. Ribosomes:
- Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, either free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
8. Lysosomes:
- Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down cellular waste and debris, playing a vital role in cell cleanup and recycling.
9. Vacuoles:
- Vacuoles are storage organelles that can contain water, nutrients, or waste materials.
10. Chloroplasts (in plant cells):
- Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy (glucose) in plant cells.
11. Cell Wall (in plant cells):
- The cell wall provides structural support and protection to plant cells, located outside the cell membrane.
12. Centrioles (in animal cells):
- Centrioles are involved in cell division and help organize microtubules for the formation of the mitotic spindle.
Let’s practice!

