Reflection Of Sound
Key Notes:
1️⃣ What is Reflection of Sound?
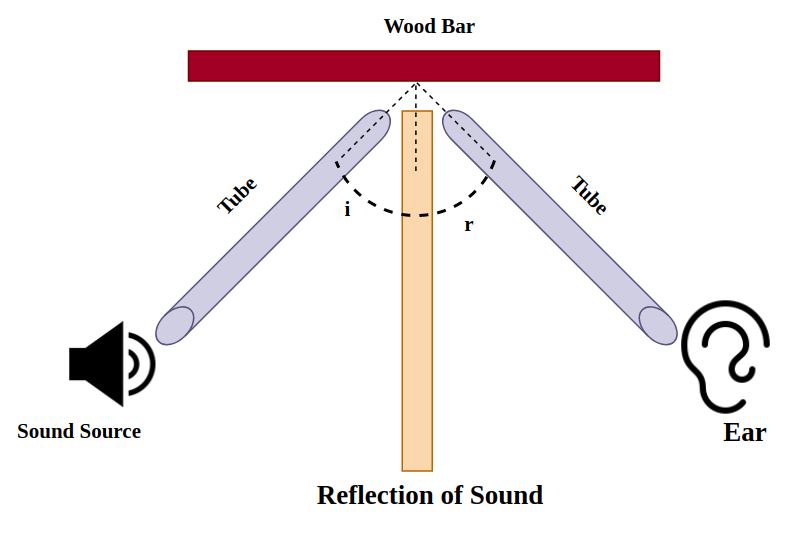
- Reflection of sound is the bouncing back of sound waves when they strike a hard surface like a wall, cliff, or building.
- It is similar to the reflection of light but involves sound waves.
2️⃣ Laws of Reflection of Sound
The reflection of sound follows the same laws as light:
- Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
- The incident sound wave, reflected sound wave, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
3️⃣ Echo 🎤
- An echo is the repetition of sound heard after it reflects from a distant surface.
- For an echo to be heard clearly:
- Time gap ≥ 0.1 seconds
- Distance of reflecting surface ≥ 17 meters (in air)
- Example: Shouting near a hill or inside a large empty hall.
4️⃣ Multiple Reflection of Sound
- When sound reflects more than once, it is called multiple reflection.
- Examples:
- Sound in concert halls
- Megaphones, loudhailers
- Stethoscope
5️⃣ Uses of Reflection of Sound
- SONAR: Used to measure depth of the sea and locate underwater objects.
- Stethoscope: Helps doctors hear heartbeats.
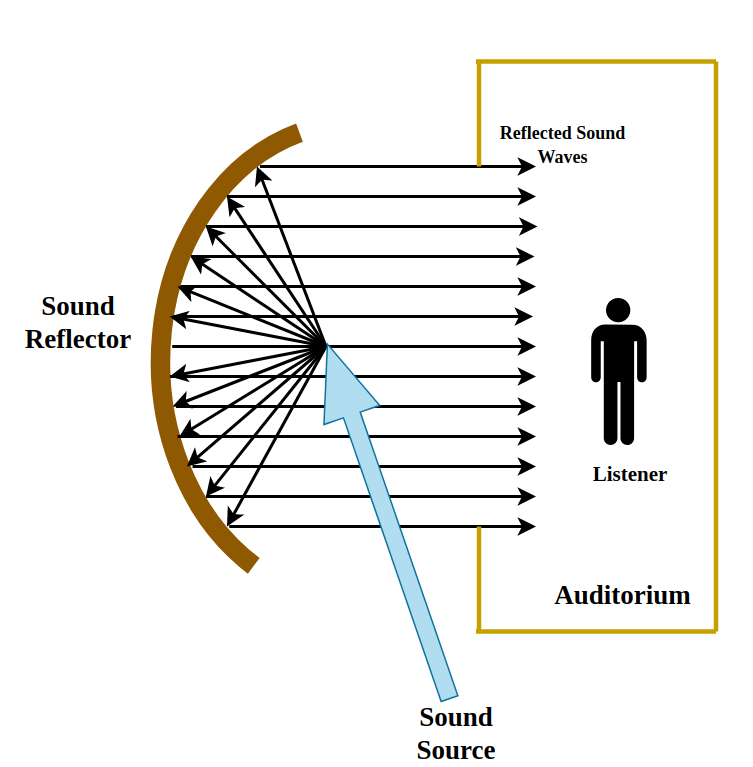
- Soundboards in auditoriums help distribute sound evenly.
6️⃣ Reverberation 🔁
- Reverberation is the persistence of sound caused by repeated reflections in an enclosed space.
- Too much reverberation makes sound unclear.
- Reduced by using:
- Curtains
- Carpets
- Acoustic panels
7️⃣ Difference Between Echo and Reverberation
| Echo | Reverberation |
|---|---|
| Heard as a distinct sound | Sound overlaps and continues |
| Requires large distance | Occurs in enclosed spaces |
| Time gap ≥ 0.1 s | Time gap < 0.1 s |
8️⃣ Important Exam Points ⭐
- Reflection of sound helps us hear sounds clearly in halls.
- Hard surfaces reflect sound better than soft surfaces.
- Used in medical, marine, and communication fields.
Let’s practice!

