Propagation Of Sound
Key Notes:


📌 What is Sound?
- Sound is a form of energy that produces the sensation of hearing.
- It is produced due to the vibrations of objects.
📌 How Does Sound Travel?
- Sound travels in the form of waves.
- It moves through a medium (solid, liquid, or gas).
- Sound cannot travel in a vacuum 🚫.
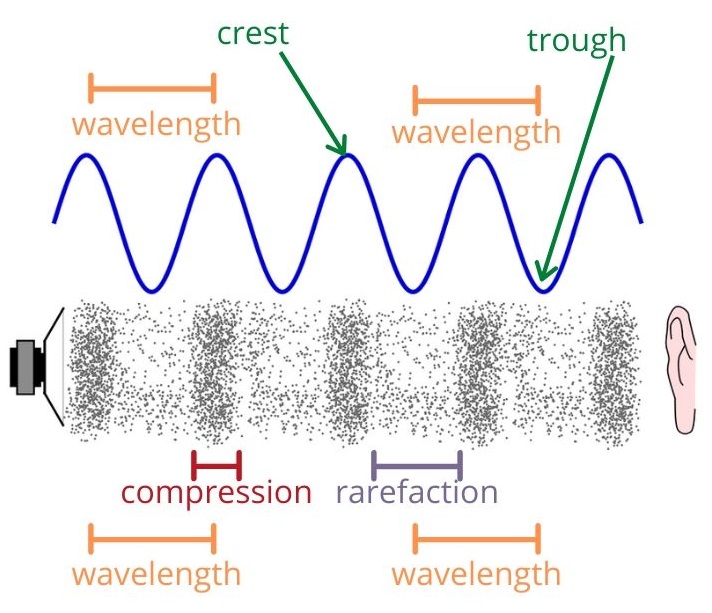
📌 Type of Sound Wave
- Sound waves are longitudinal waves.
- Particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction as the wave travels.
📌 Compression and Rarefaction
- Compression (C):
- Region where particles are closer together.
- High pressure and high density.
- Rarefaction (R):
- Region where particles are far apart.
- Low pressure and low density.
- A sound wave consists of alternate compressions and rarefactions.
📌 Medium Required for Propagation
- Sound can travel through:
- Solids (fastest) 🪨
- Liquids
- Gases (slowest)
- Speed of sound depends on the nature of the medium.
📌 Speed of Sound
- Speed of sound in air at room temperature ≈ 343 m/s.
- Sound travels:
- Fastest in solids
- Slower in liquids
- Slowest in gases
📌 Sound Energy Transfer
- Sound transfers energy, not matter.
- Particles only vibrate around their mean positions.
📌 Example of Sound Propagation
- When a bell rings 🔔:
- Bell vibrates → air particles vibrate → vibrations reach our ears → sound is heard.
📌 Important Points to Remember
- Sound needs a material medium.
- Sound waves are mechanical waves.
- No sound is heard in outer space 🚀.
Let’s practice!

