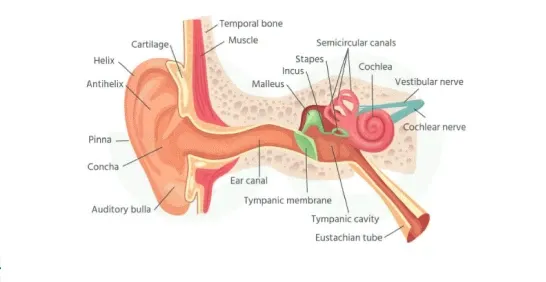
structure of human ear
Key Notes:


🔹 Overview
- The human ear is the organ of hearing and balance.
- It has three main parts: Outer Ear, Middle Ear, and Inner Ear.
1️⃣ Outer Ear
Parts:
- Pinna (Auricle): Collects sound waves.
- Auditory canal (Ear canal): Carries sound to the eardrum.
Function:
- Collects and directs sound waves toward the eardrum.
2️⃣ Middle Ear
Parts:
Eardrum (Tympanic membrane): Vibrates when sound waves strike it.
Three tiny bones (Ossicles):
- Malleus (Hammer)
- Incus (Anvil)
- Stapes (Stirrup)
Eustachian tube: Connects middle ear to the throat.
Function:
- Amplifies sound vibrations and transmits them to the inner ear.
- Eustachian tube helps maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
3️⃣ Inner Ear
Parts:
- Cochlea: Spiral-shaped, filled with fluid.
- Semicircular canals: Three loop-like structures.
- Auditory (Vestibulocochlear) nerve
Function:
- Cochlea: Converts sound vibrations into nerve impulses (hearing).
- Semicircular canals: Maintain balance and posture.
- Auditory nerve: Carries impulses to the brain.
🧠 How We Hear (In Short)
- Sound enters the outer ear.
- Vibrations pass through the eardrum and ossicles.
- The cochlea converts vibrations into nerve signals.
- The brain interprets these signals as sound.
⭐ Exam Tips
- Remember the order: Pinna → Eardrum → Ossicles → Cochlea → Brain
- Learn the names of ossicles in order: Malleus → Incus → Stapes
- Inner ear = Hearing + Balance
Let’s practice!

