Applications Of Ultrasound
Key Notes:
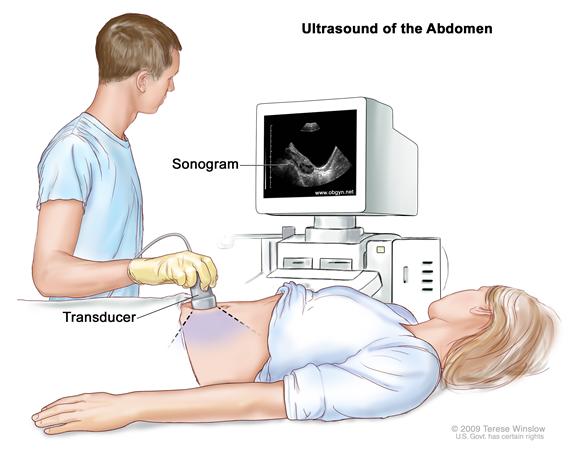


🔹 What is Ultrasound?
- Ultrasound consists of sound waves with frequencies higher than 20,000 Hz (above human hearing).
- These waves can travel through solids and liquids and get reflected from different surfaces.
🏥 Medical Applications
- Ultrasonography: Used to see internal organs like liver, kidneys, and uterus.
- Pregnancy scans: Helps monitor the growth and health of the baby.
- Detecting stones: Used to locate kidney stones and gallstones.
- Echocardiography: Creates images of the heart to check blood flow and heart function.
- Therapeutic ultrasound: Helps in breaking kidney stones into smaller pieces (lithotripsy).
🏭 Industrial Applications
- Detecting cracks and flaws: Finds internal defects in metal blocks and machine parts.
- Thickness measurement: Measures the thickness of sheets and pipes.
- Cleaning: Used to clean delicate instruments like electronic components and surgical tools.
🌊 Navigation & Research
- SONAR (Sound Navigation and Ranging):
- Used to measure sea depth.
- Helps locate underwater objects like submarines and shipwrecks.
- Used by fishermen to detect schools of fish.
🔬 Other Uses
- Welding plastics: Ultrasound is used to join plastic parts.
- Animal studies: Helps observe internal organs of animals without surgery.
✅ Key Advantages
- Non-invasive and painless
- Does not use harmful radiation
- Provides real-time images
🧠 Quick Recall
- Ultrasound frequency: > 20 kHz
- Medical imaging device: Ultrasound scanner
- Underwater detection system: SONAR
Let’s practice!

