Rate Of Doing Work
Key Notes:
Definition of Work:
- Work is done when a force is applied to an object, and the object moves in the direction of the force.
- Formula: W = F × d × cos θ where:
- W is work,
- F is force,
- d is displacement,
- θ is the angle between force and displacement.
Rate of Doing Work:
- The rate at which work is done is called power.
- Power measures how quickly or slowly work is performed.
Definition of Power:
- Power is defined as the amount of work done per unit time.
- Formula: P = W/t
- P is power,
- W is work done,
- t is the time taken.
Unit of Power:
- The SI unit of power is the watt (W).
- 1 watt = 1 joule / second (J/s)
Larger Units of Power:
- Kilowatt (kW): 1 kW = 1000 W.
- Horsepower (hp): 1 hp ≈ 746 W.
Energy and Power:
- Power is closely related to energy transfer.
Energy transferred = Power × Time
Practical Examples:
- A person climbing stairs at different speeds demonstrates different rates of doing work.
- Electrical appliances like bulbs and motors have power ratings that indicate the energy they consume per unit time.
Relation to Efficiency:
- Power and work are used to calculate the efficiency of machines, which is given by:
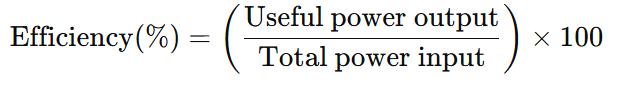
Graphical Representation:
- Work versus time graphs can help visualize power, as the slope of the graph gives the power.
Factors Affecting Power:
- The amount of work done.
- The time taken to do the work.
Let’s practice!

