Energy
Key Notes:
- What is Energy?
- Energy is the ability to do work or cause a change in an object or system.
- It exists in various forms and can be neither created nor destroyed, only transformed from one form to another (Law of Conservation of Energy).
A. Forms of Energy:
- Kinetic Energy: Energy of motion. It depends on an object’s mass and velocity.
- Potential Energy: Stored energy due to an object’s position or condition. Common types include gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy.
- Types of Energy:
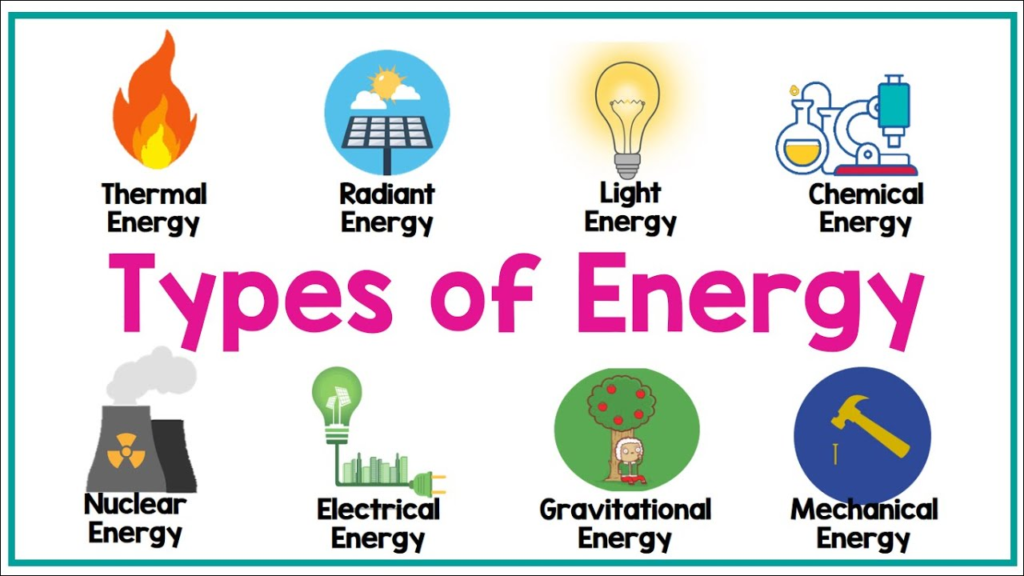
- Mechanical Energy: The sum of an object’s kinetic and potential energy.
- Thermal (Heat) Energy: The energy associated with the motion of particles in a substance. It is related to temperature.
- Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. Released during chemical reactions.
- Electrical Energy: Energy carried by moving electrons (electricity).
- Nuclear Energy: Released during nuclear reactions, such as fission and fusion.
- Sound Energy: Energy produced by vibrating objects that create sound waves.
- Light (Radiant) Energy: Energy carried by electromagnetic waves (photons).
2. Conversion of Energy:
- Energy can change from one form to another. For example, potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy when an object falls.
3. Law of Conservation of Energy:
- The total energy in a closed system remains constant. Energy may change forms but is not created or destroyed.
4. Energy Sources:
- Renewable Energy: Derived from sources that are naturally replenished, e.g., solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy.
- Non-Renewable Energy: Derived from finite sources like fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and nuclear fuel.
5. Energy Efficiency:
- Measures how well energy is converted from one form to another. High efficiency means less energy is wasted.
6. Environmental Impact:
- The choice of energy sources can have environmental consequences, including air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction.
7. Energy Conservation:
- Reducing energy usage through efficient appliances, insulation, and responsible consumption habits.
8. Global Energy Challenges:
- Meeting the growing demand for energy while minimizing environmental impact is a global challenge.
- Transitioning to sustainable and renewable energy sources is a critical goal.
9. Energy Units:
- Energy is measured in units such as joules (J) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
10. Energy in Everyday Life:
- Energy is a fundamental part of our daily lives, used for heating, transportation, electricity, and much more.
Let’s practice!

