Evaporation
key notes :
Definition:
- Evaporation is the process by which a liquid changes into a gas at a temperature below its boiling point.
How It Happens:
- Molecules at the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to overcome intermolecular forces and escape into the air as vapor.
Factors Affecting Evaporation:
- Surface Area: Greater surface area increases evaporation rate as more molecules are exposed.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures provide more energy for molecules to escape.
- Humidity: Lower humidity levels lead to faster evaporation since the air can hold more water vapor.
- Wind Speed: Increased wind removes water vapor from the surface, enhancing evaporation.
- Nature of Liquid: Volatile liquids evaporate more quickly than non-volatile ones.
Cooling Effect:
- Evaporation causes cooling because high-energy molecules leave the liquid, reducing the average kinetic energy of the remaining molecules.
Real-Life Examples:
- Sweating helps cool the body as the sweat evaporates.
- Clothes dry faster on a sunny or windy day.
- Water bodies lose heat through evaporation.
Applications:
- Refrigeration systems use the principle of evaporation for cooling.
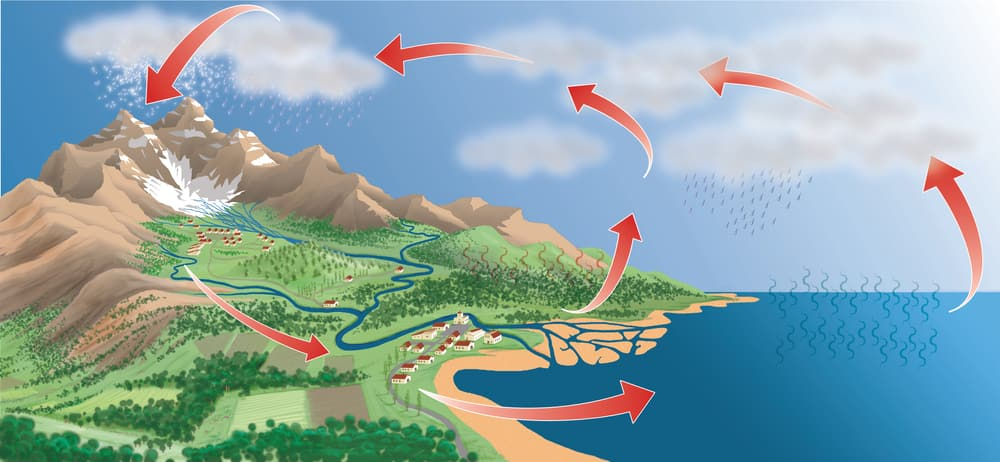
- Evaporation is a key step in the water cycle, contributing to cloud formation.
Differences from Boiling:
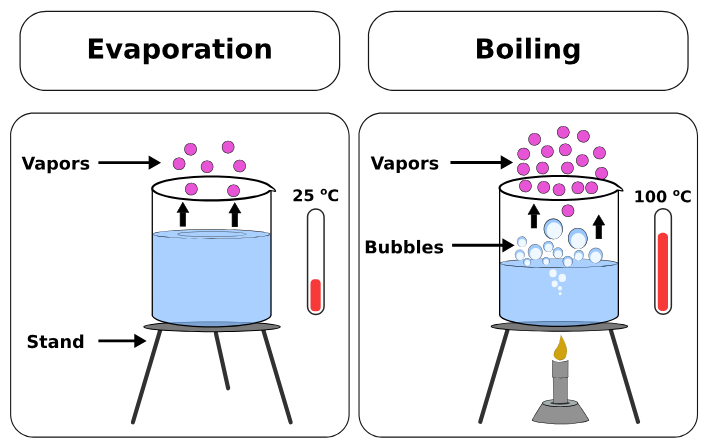
- Evaporation occurs at any temperature, while boiling happens at a specific boiling point.
- Evaporation occurs only at the surface, whereas boiling occurs throughout the liquid.
Role in Nature:
- Maintains the Earth’s temperature balance by absorbing heat.
- Facilitates the movement of water from oceans and lakes to the atmosphere.
Importance in Industry:
- Used in processes like salt production (evaporation of seawater).
- Applied in drying techniques for food and pharmaceuticals.
Let’s practice!

