States Of Matter
Key Notes:
Definition of Matter:
- Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass.
- It is made up of tiny particles that are in constant motion.
Three States of Matter:

- Solid:
- Particles are tightly packed in a fixed arrangement.
- Strong intermolecular forces.
- Definite shape and volume.
- Particles vibrate in place but do not move freely.
- Liquid:
- Particles are loosely packed, allowing them to flow.
- Weaker intermolecular forces compared to solids.
- Definite volume but no fixed shape (takes the shape of the container).
- Particles can move past each other.
- Gas:
- Particles are far apart with minimal intermolecular forces.
- No definite shape or volume (expands to fill the container).
- Particles move freely and at high speeds.
Interconversion of States of Matter:
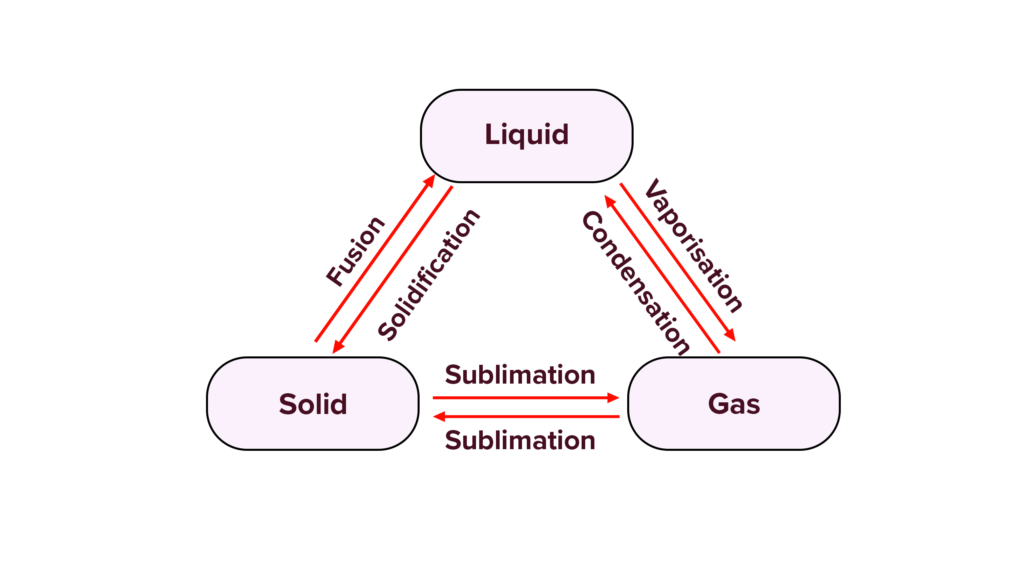
- Processes:
- Melting: Solid to liquid.
- Freezing: Liquid to solid.
- Vaporization: Liquid to gas.
- Condensation: Gas to liquid.
- Sublimation: Solid to gas without becoming a liquid.
- Deposition: Gas to solid without becoming a liquid.
- Effect of Temperature and Pressure:
- Increasing temperature adds energy to particles, overcoming intermolecular forces.
- Increasing pressure can compress particles, changing the state.
Characteristics of Particles of Matter:
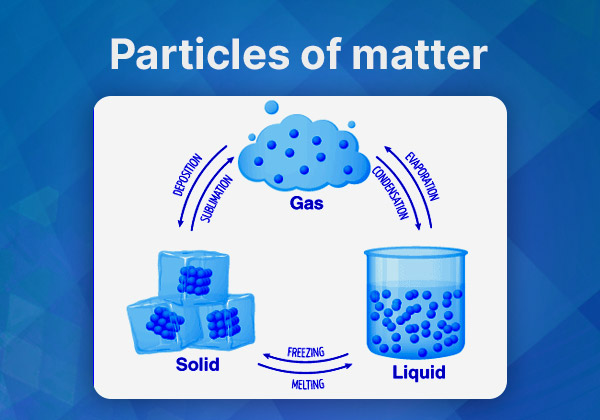
- Particles have spaces between them.
- Particles are continuously in motion.
- Particles attract each other with varying forces.
Plasma and Bose-Einstein Condensate:
- Plasma: High-energy state of matter where particles are ionized (e.g., stars, lightning).
- Bose-Einstein Condensate: Extremely low-temperature state where particles behave as a single quantum entity.
Kinetic Molecular Theory:
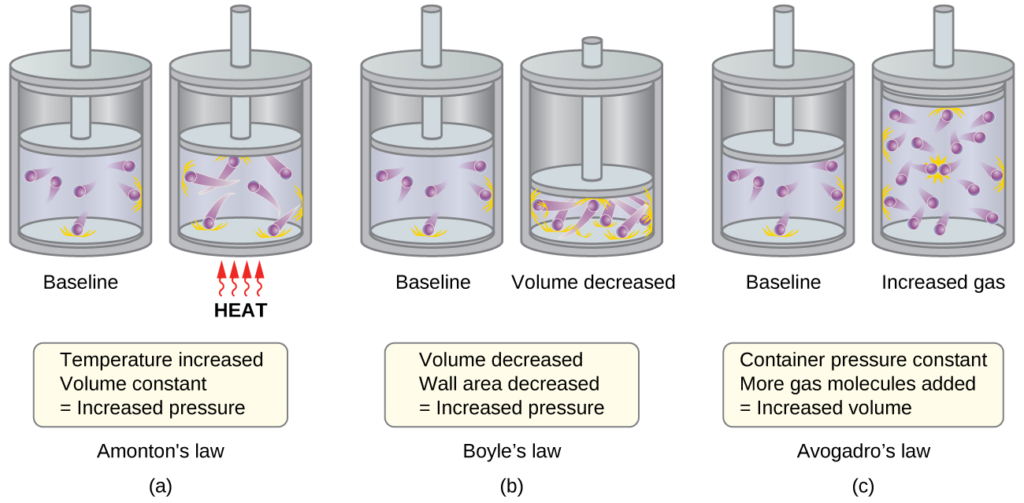
- Explains the behavior of matter based on particle motion.
- Higher temperature increases kinetic energy, causing particles to move faster.
Applications:
- Liquefaction of gases (e.g., oxygen for medical use).
- Cryogenics (preservation of biological samples).
- Refrigeration and air conditioning (state changes of refrigerants).
Examples from Daily Life:
- Ice melting in a drink (solid to liquid).
- Steam from boiling water (liquid to gas).
- Dry ice subliming into gas (solid to gas).
Significance in Science:
- Understanding states of matter is crucial for studying physics, chemistry, and material science.
Let’s practice!

