Inscribed angles
key notes :
🔵 What is an Inscribed Angle?
An inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex lies on the circle, and its sides (arms) touch the circle.
👉 It “sits” on the circle’s boundary.
🔴 Intercepted Arc 🎯
The intercepted arc is the part of the circle cut off or covered by the inscribed angle.
🟢 Inscribed Angle Theorem 💡
The measure of an inscribed angle = ½ × measure of the intercepted arc.
📌 If the arc is 80°, the inscribed angle is 40°.
🟣 Angles on the Same Arc Are Equal ⚖️
If two inscribed angles intercept the same arc, they have the same measure.
🟠 Angle in a Semicircle = 90° ⭕
If the endpoints of an inscribed angle lie on the diameter, the angle is a right angle (90°).
👉 Also called Thales’ Theorem.
🟡 Inscribed vs. Central Angles 🆚
- Central angle = vertex at the center; equals the arc.
- Inscribed angle = vertex on the circle; equals half of the arc.
📌 Example: If a central angle is 100°, the inscribed angle on the same arc is 50°.
🔵 Useful for Solving Problems ✏️
You can use inscribed angles to find:
✔ Missing angle measures
✔ Arc lengths
✔ Right triangles inside circles
✔ Relations with central angles
Learn with an example
What is ∠HGI?
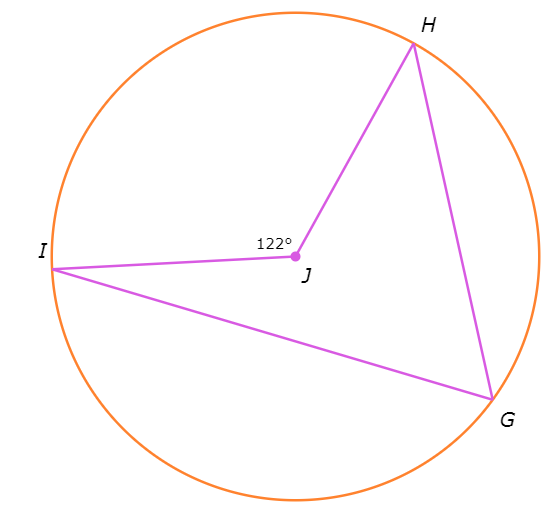
∠HGI= _____∘
Look at the diagram:
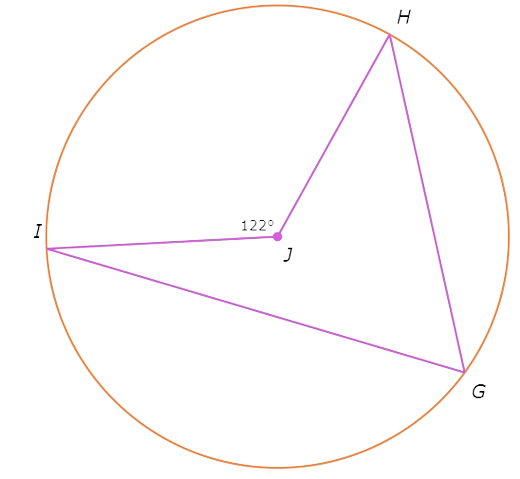
∠HGI is an inscribed angle that intercepts the same arc as the central angle ∠J, so use the Inscribed Angle Theorem.
∠HGI =1/2 . ∠j
=1/2 (122°) plug ∠J=122°
=61°
∠HGI is 61°.
What is ∠F?
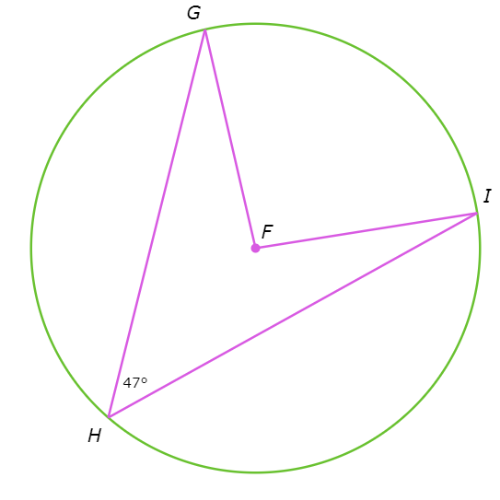
∠F= ________°
Look at the diagram:
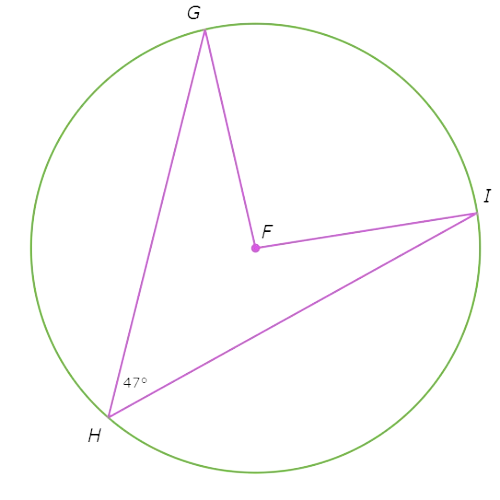
∠GHI is an inscribed angle that intercepts the same arc as the central angle ∠F, so use the Inscribed Angle Theorem.
∠F= 2 . ∠GHI Inscribed Angle Theorem
= 2 .(47°) Plug in ∠GHI=47°
= 94° Multiply
∠F is 94°.
What is ∠J?
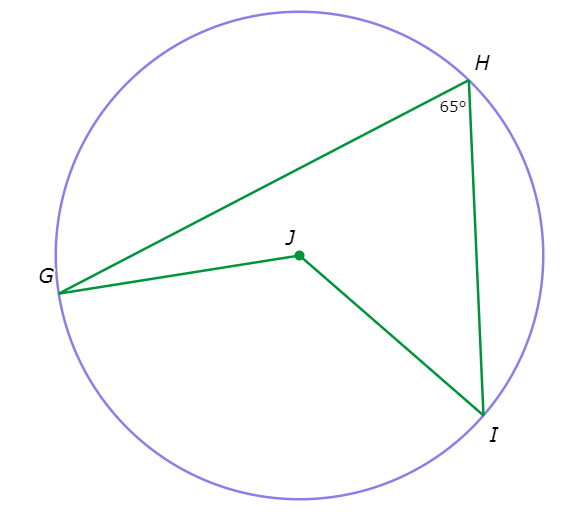
∠J=______ °
Look at the diagram:
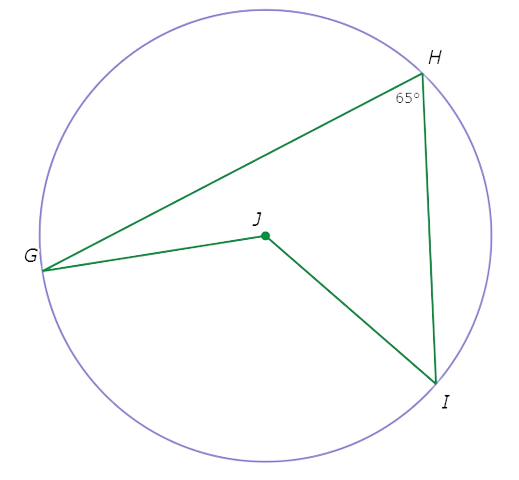
∠GHI is an inscribed angle that intercepts the same arc as the central angle ∠J, so use the Inscribed Angle Theorem.
∠J = 2 . ∠GHI Inscribed Angle Theorem
= 2 . (65°) Plug in ∠GHI=65°
= 130° Multiply
∠J is 130°.
let’s practice!

