Perimeter of polygons with an inscribed circle
Key Notes :
🟢 What is an Inscribed Circle (Incircle)?
- A circle drawn inside a polygon that touches all its sides.
- The point where the circle touches a side is called the point of tangency.
- The center of the circle is called the incenter (🔺 for triangles).
🟣 Key Property of Tangents from a Point
👉 If two tangents are drawn from the same vertex to the circle,
then they are equal in length.
Example in a quadrilateral:
- From vertex A, the two tangent lengths are AP = AS.
- From vertex B, the two tangent lengths are BP = BQ, and so on.
This property is the secret behind finding the perimeter! 🔑✨
🔵 How Perimeter Is Found Using Tangent Lengths
Each side of the polygon is formed by adding two tangent segments,
one from each of its endpoints.
Example for a quadrilateral ABCD:
- Side AB = AP + BP
- Side BC = BQ + CQ
- Side CD = CR + DR
- Side DA = DS + AS
🟠 Amazing Result: Perimeter = Sum of All Tangent Lengths × 2
Since every tangent length repeats twice (once for each side),
the perimeter = (AP + BP + CQ + DR + …) × 2.
🟢 Special Case — Triangle
For a triangle, if tangent lengths are x, y, z at three vertices,
then:
- Perimeter = x + y + z + x + y + z = 2(x + y + z)
- Or simpler:
➤ Perimeter = sum of the three sides (as usual!)
because each side is formed by adding tangent lengths.
🔴 Formula Summary ✨
⭐ Perimeter of polygon with an inscribed circle
P = 2(x1 + x2 + x3 + …)
where x1 , x2 , x3… are tangent lengths from each vertex.
🟣 Visual Shortcut
- Tangent lengths from each vertex are equal.
- Add all tangent lengths.
- Multiply by 2.
- 🎉 You get the perimeter!
🟡 Why Useful?
This method is useful when:
✔ Side lengths are not given
✔ Tangent lengths (from vertices to points of tangency) are provided
Learn with an example
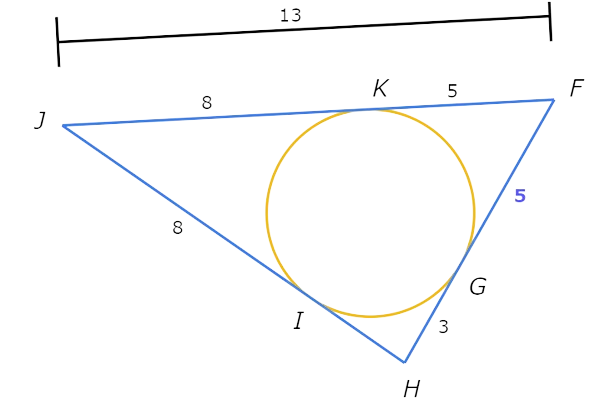
What is FG?
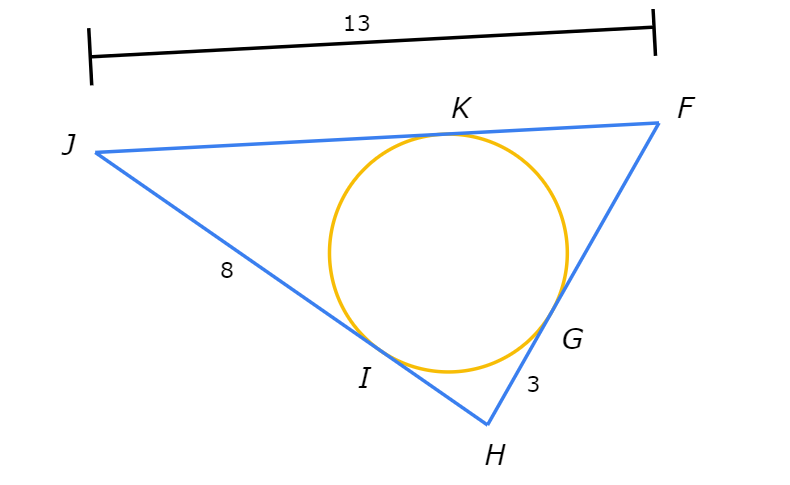
FG= _______
Look at the diagram:
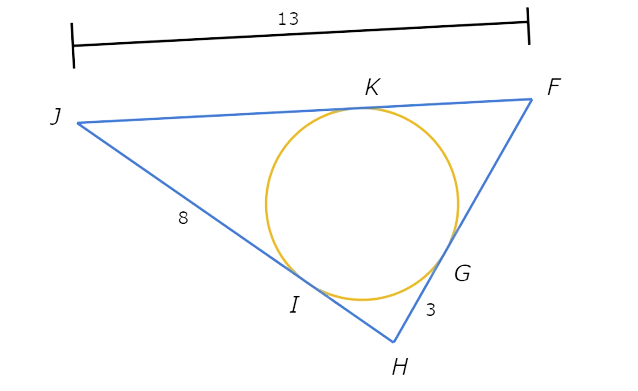
Find the unknown segment lengths.
JK and IJ are tangents to the inscribed circle from J. So , JK is congruent to IJ.
JK=IJ=8.
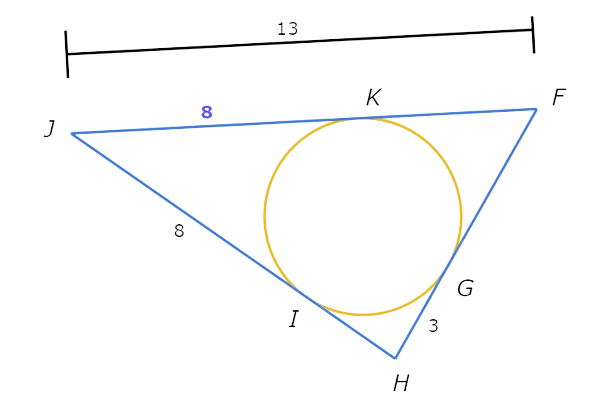
You know JK and FJ. Use the Additive Property of Length to write an equation and find FK.
FK+JK= FJ Additive Property of Length
FK + 8 = 13 Plug in JK=8 and FJ=13
FK = 5 Subtract 8 from both sides
So, FK is 5.
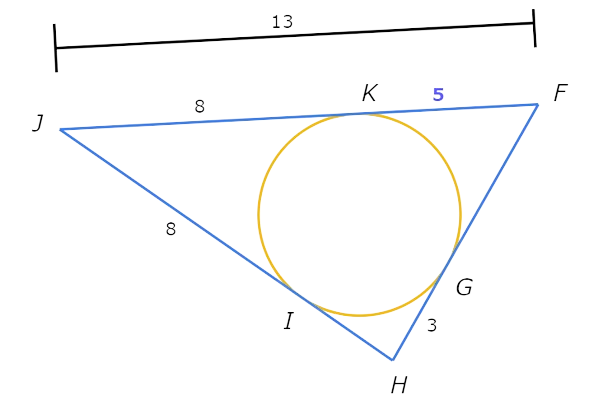
FG and FK are tangents to the inscribed circle from F. So , FG is congruent to FK.
FG=FK=5.
What is TU?
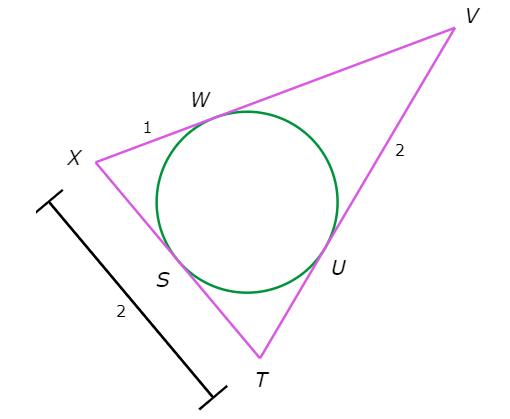
TU=______
Look at the diagram:
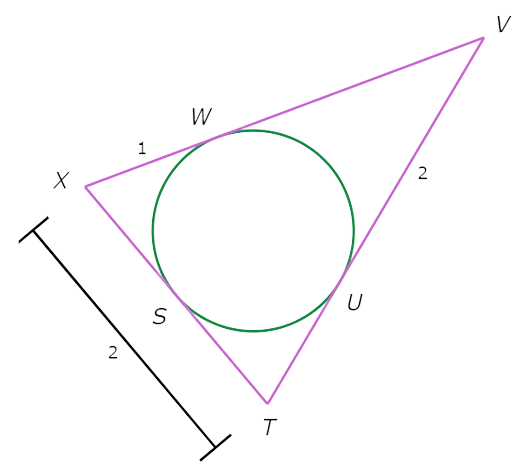
Find the unknown segment lengths.
SX and WX are tangents to the inscribed circle from X. So , SX is congruent to WX .
SX=WX=1.
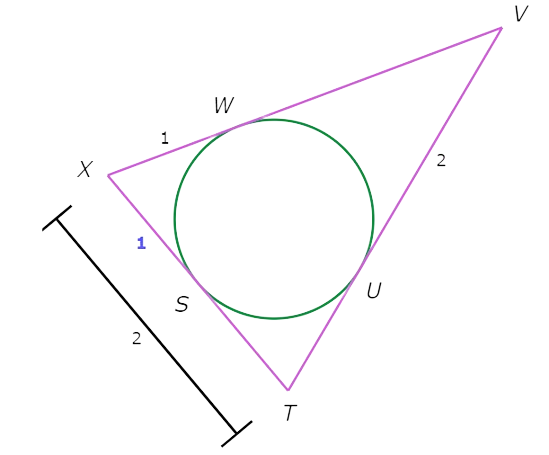
You know SX and TX. Use the Additive Property of Length to write an equation and find ST.
SX + ST = TX Additive Property of Length
1 + ST = 2 Plug in SX=1 and TX=2
ST= 1 Subtract 1 from both sides
So, ST is 1.
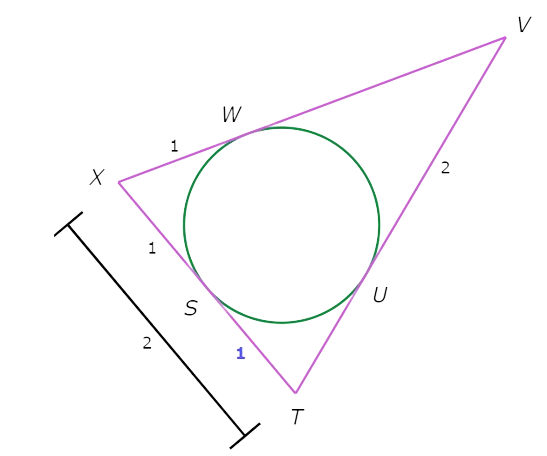
TU and ST are tangents to the inscribed circle from T. So , TU is congruent to ST.
TU=ST=1.
let’s practice!

