Tangent lines
Key Notes :
🔵 What is a Tangent Line?
A tangent line is a straight line that touches a circle at exactly one point.
👉 This point is called the point of tangency.
🎯 It does not cut across the circle.
🟢 Tangent Touches Only Once
A tangent line meets the circle in only one point.
✔️ If it crosses the circle in two points, it becomes a secant, not a tangent.
🔴 Radius and Tangent Are Perpendicular
At the point where the tangent touches the circle:
👉 The radius is always perpendicular (90°) to the tangent line.
📐 Radius ⟂ Tangent
🟣 Tangents from an External Point
If you draw two tangent lines from the same outside point,
✔️ The two tangent lengths are equal.
🎯 This is called tangent segments theorem.
🟡 Real-Life Examples of Tangents
✨ Wheel touching the road
✨ Bike tire touching ground
✨ A ladder leaning gently against a round pole (touches at one point)
🔵 Tangent Formula (Basic Idea)
If P is an external point and you draw tangents to a circle that touch at A and B:
👉 PA = PB
🟠 Difference Between Tangent and Secant
| Line Type | Touches Circle | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Tangent | 1 point | Just touches |
| Secant | 2 points | Cuts across |
🎉 Summary
- A tangent touches the circle at one point only.
- Radius to the tangent is 90°.
- Tangents from the same point are equal in length.
- Used in circles, wheels, and geometry constructions.
Learn with an example
UV is tangent to ⨀T. What is ∠W?
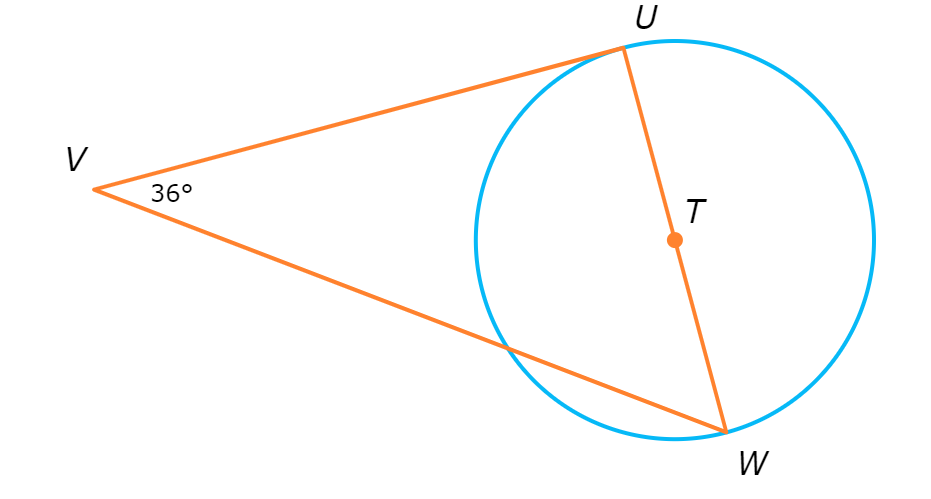
∠W = ________°
Look at the diagram.
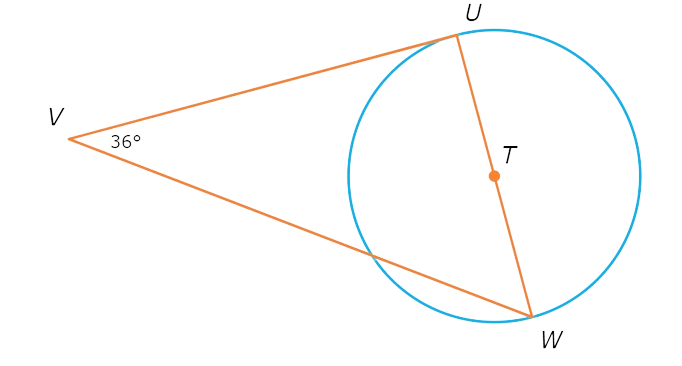
Since UV is tangent to ⨀T, △UVW is a right triangle with right angle ∠U. So, ∠W and ∠V are complementary. Write an equation setting the sum of their measures equal to 90°, and solve for ∠W.
∠W + ∠V = 90°
∠W + 36° = 90° Plug in ∠V=36°
∠W = 54° Subtract 36° from both sides
∠W is 54°.
PQ is tangent to ⨀N. What is ∠Q?
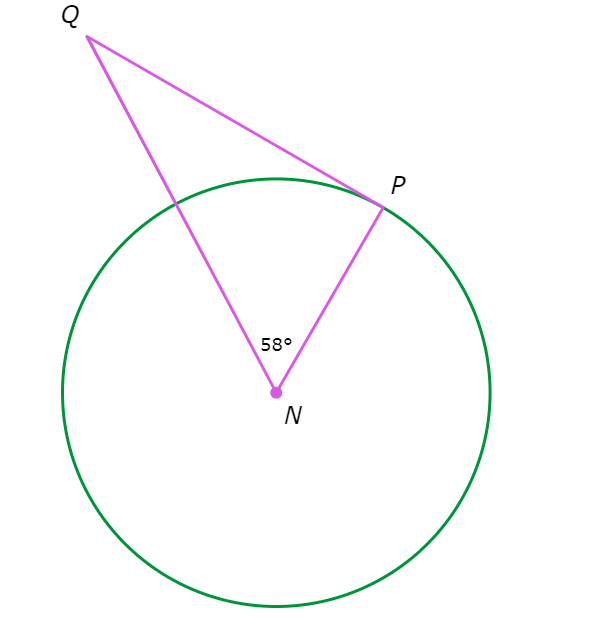
∠Q = ________°
Look at the diagram.
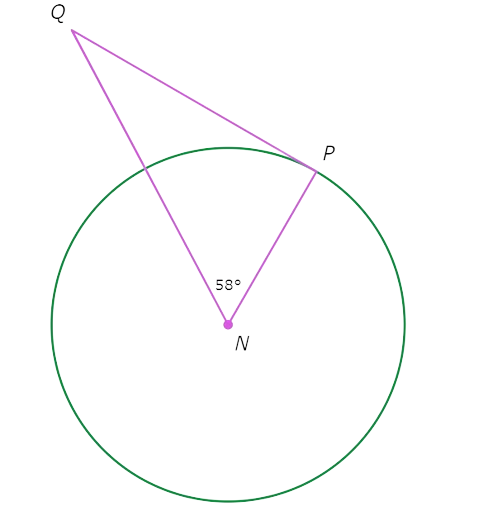
Since PQ is tangent to ⨀N, △NPQ is a right triangle with right angle ∠P. So, ∠N and ∠Q are complementary. Write an equation setting the sum of their measures equal to 90°, and solve for ∠Q.
∠N + ∠Q = 90°
58° + ∠Q = 90° Plug in ∠N=58°
∠Q = 32° Subtract 58° from both sides
∠Q is 32°.
PQ is tangent to ⨀N. What is NQ?
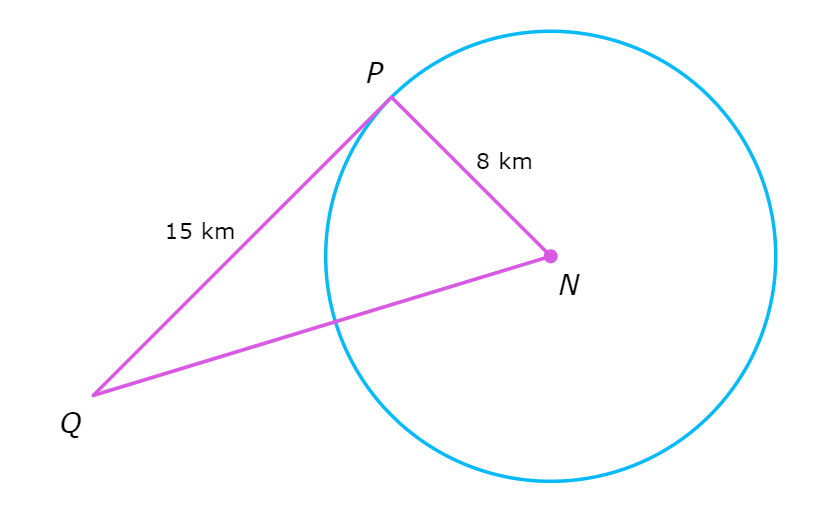
NQ = ________km
Since PQ is tangent to ⨀N , PQ is perpendicular to NP. So, △NPQ is a right triangle with hypotenuse NQ.

Now use Pythagoras’ theorem to find NQ.
NP2 + PQ2 = NQ2
82 + 152 = NQ2 Plug in NP=8 and PQ=15
64 + 225 = NQ2 Square
289 = NQ2 Add
17 = NQ Take the square root of both sides
NQ is 17 kilometres.
Let’s practice !

