Angles in inscribed right triangles
Key Notes :
🔹 Inscribed Triangle Definition
An inscribed triangle is a triangle whose all vertices lie on a circle.
👉 This circle is called the circumcircle.
🔹 Right Triangle in a Circle
A right triangle can always be inscribed in a circle.
✨ The hypotenuse becomes the diameter of the circle.
🟢 Important Rule:
➡️ If a triangle is inscribed in a circle and one side is the diameter,
then the angle opposite the diameter is a right angle (90°).
🔹 Thales’ Theorem 🎯
This amazing theorem states:
👉 Any angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle (90°).
So, if you see a triangle inside a circle with one side as diameter → 90° for sure! ✔️
🔹 Angle Relationships
In an inscribed right triangle:
- The right angle is opposite the diameter
- The other two angles are acute angles
- These two acute angles add up to 90°
🧩 Example: If one angle is 30°, the other must be 60°.
🔹 Central Angle vs Inscribed Angle 🔵📐
An inscribed angle is half of the central angle that subtends the same arc.
👉 In a right triangle, the arc corresponding to the right angle is a semicircle (180°).
So, inscribed angle = 180° ÷ 2 = 90° 👍
🔹 Identifying Right Angles in Diagrams 👀
If you spot:
- A triangle inside a circle
- One side as the diameter
🎉 Then you instantly know the angle opposite is 90°!
🔹 Real-World Uses 🌍
Inscribed right triangles help in:
- Finding missing angles
- Solving circle geometry problems
- Understanding trigonometry basics
- Proving theorems in coordinate geometry
🌈 Summary
📌 The hypotenuse of an inscribed right triangle is always the diameter.
📌 The angle opposite that diameter is always 90°.
📌 The other two angles are acute and complementary.
📌 This is based on Thales’ Theorem.
Learn with an example
🔔 What is ∠K?
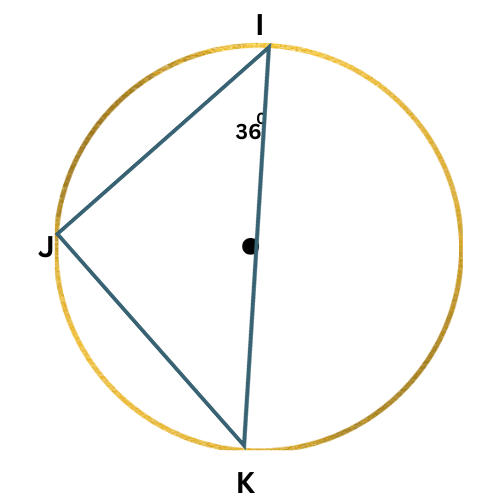
∠K=______ °
Since IK is a diameter of the circle, ∠J is a right angle.
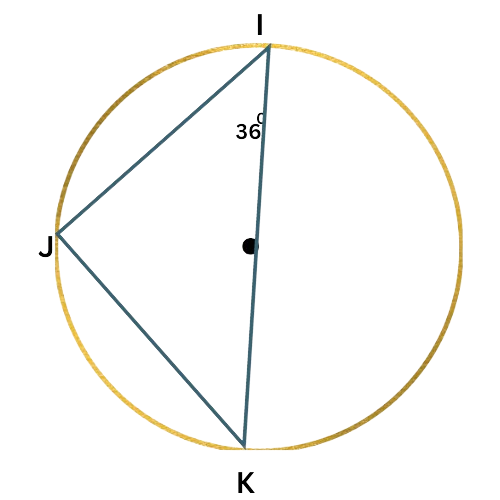
So, △IJK is a right triangle and ∠I and ∠K are complementary. Write an equation setting the sum of their measures equal to 90°, and solve for ∠K.
∠I+∠K=90°
36°+∠K=90° Plug in ∠I=36°
∠K=54° Subtract 36° from both sides
∠K is 54°.
🔔 What is ∠F?
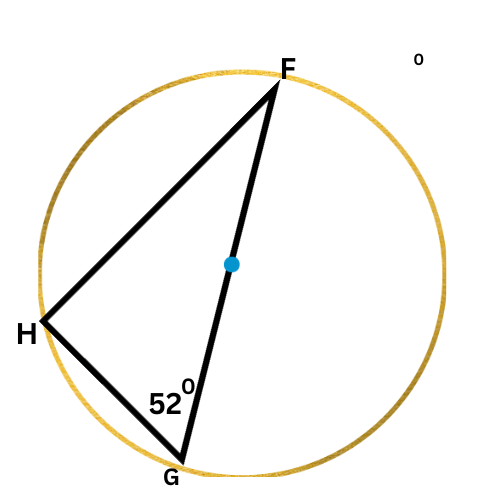
∠F=_______ °
Since FG is a diameter of the circle, ∠H is a right angle.
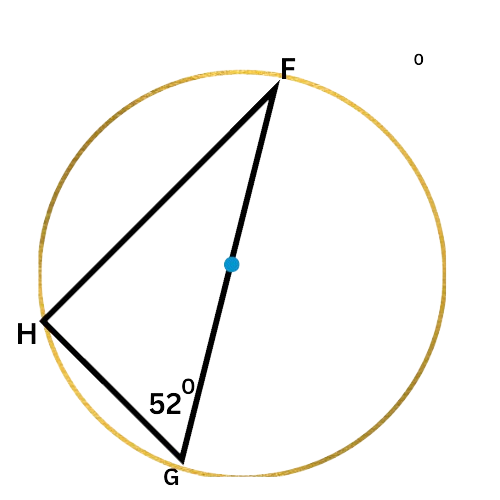
So, △FGH is a right triangle and ∠G and ∠F are complementary. Write an equation setting the sum of their measures equal to 90°, and solve for ∠F.
∠G+∠F=90°
52°+∠F=90° Plug in ∠G=52°
∠F=38° Subtract 52° from both sides
∠F is 38°.
🔔 What is ∠H?
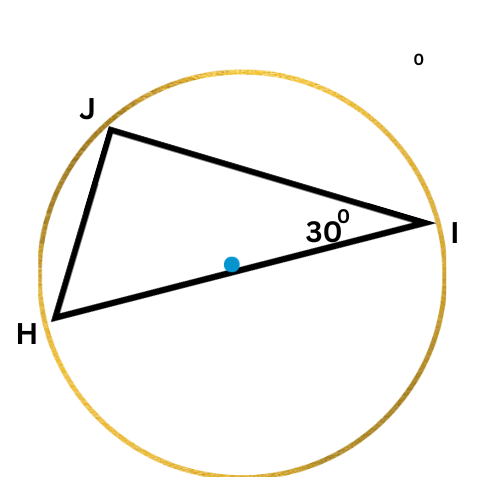
∠H=______ °
Since HI is a diameter of the circle, ∠J is a right angle.
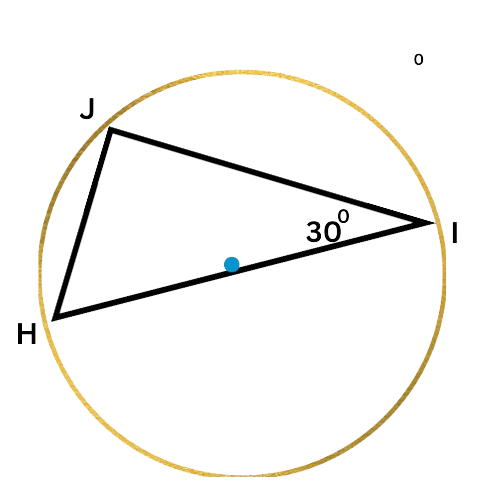
So, △HIJ is a right triangle and ∠I and ∠H are complementary. Write an equation setting the sum of their measures equal to 90°, and solve for ∠H.
∠I+∠H=90°
30°+∠H=90° Plug in ∠I=30°
∠H=60° Subtract 30° from both sides
∠H is 60°.
let’s practice!

