Parts of a circle
key Notes :
🔹 Circle
A circle is a closed curve where all points are the same distance from a fixed point.
👉 The fixed point is called the center.
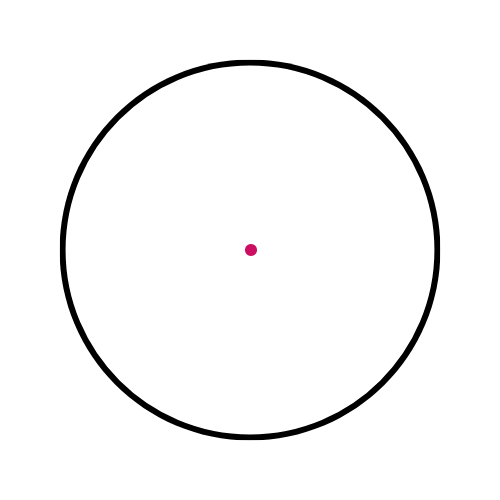
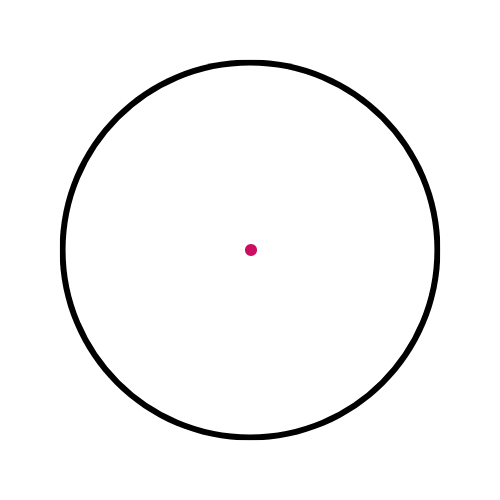
🔸 Center (O) 🎯
The middle point of the circle.
Every point on the circle is equally distant from the center.
🔹 Radius (r) 📏
A line segment from the center to any point on the circle.
All radii in a circle are equal.
Example: OA, OB
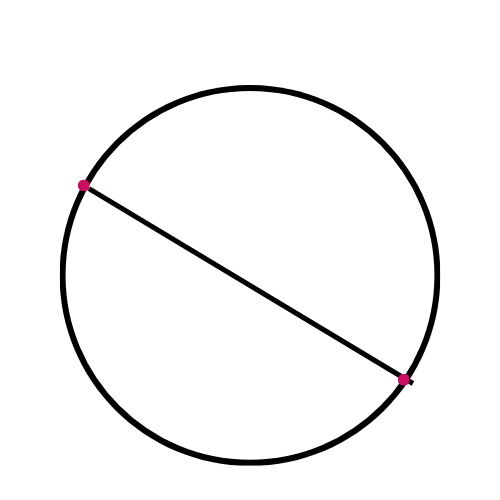
🔸 Diameter (d) 📐
A line segment that passes through the center and touches both ends of the circle.
👉 Diameter = 2 × Radius
🔹 Chord ➖
A line segment joining any two points on the circle.
👉 Every diameter is a chord, but every chord is not a diameter.
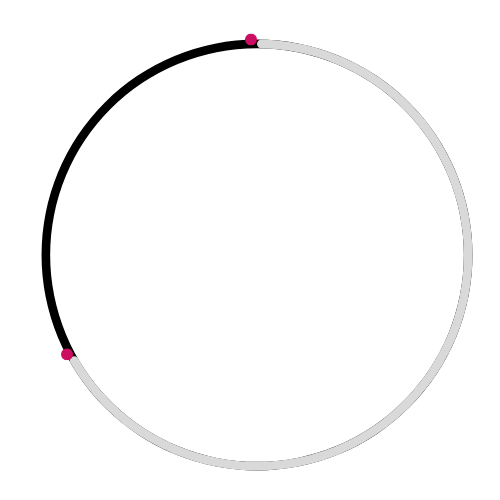
🔸 Arc 🌀
A curved part of the circle.
Types of arcs:
- Minor Arc – smaller arc
- Major Arc – larger arc
- Semi-circle – arc of 180°
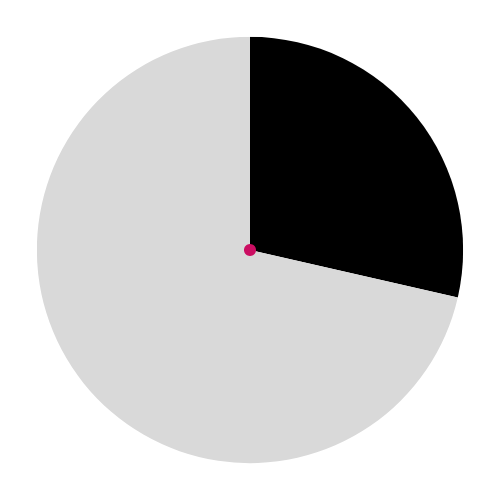
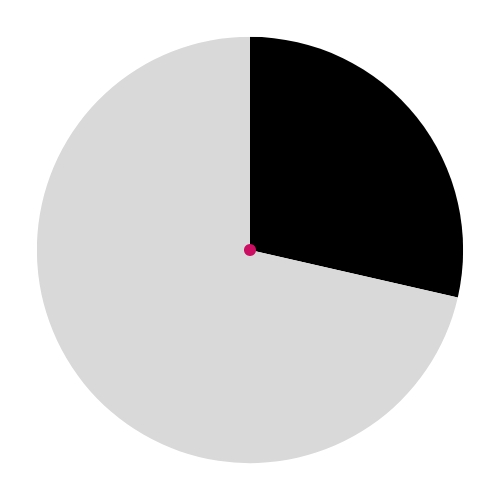
🔹 Sector 🍕
A region enclosed by two radii and the arc between them.
Looks like a pizza slice! 🍕
🔸 Segment 🟧
A region formed by a chord and its arc.
Types:
- Minor segment
- Major segment
🔹 Circumference 🔄
The boundary (perimeter) of the circle.
Formula:
👉 C = 2πr or πd
🔸 Tangent 📎
A line that touches the circle at exactly one point (point of contact).
🔹 Secant 📘
A line that cuts the circle at two points.
🔔 Summary Chart 🌟
| Part | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Center | Middle point |
| Radius | R = center → circle |
| Diameter | D = 2r |
| Chord | Joins two points |
| Arc | Curved part |
| Sector | Pizza slice area |
| Segment | Region under a chord |
| Tangent | Touches once |
| Secant | Cuts twice |
Learn with an example
Which figure shows an arc?
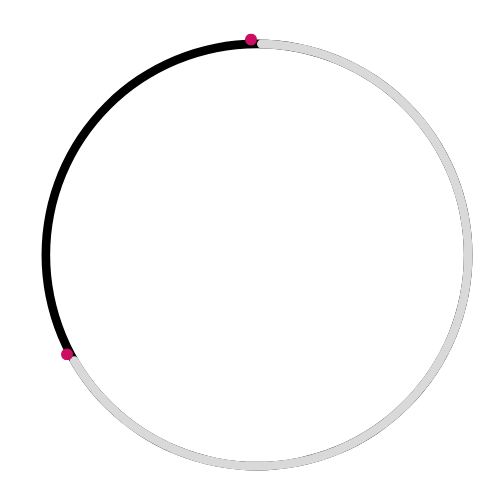
This diagram correctly shows an arc:
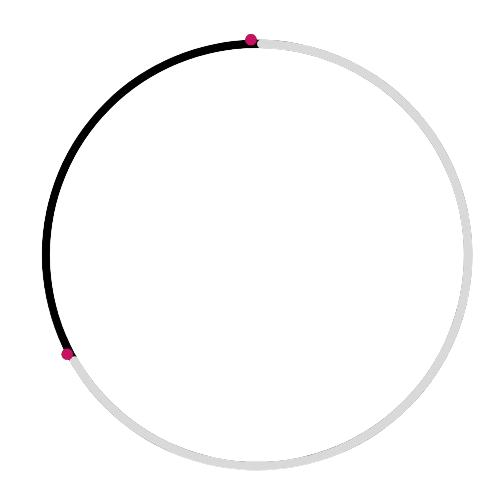
This diagram shows a sector, not an arc:
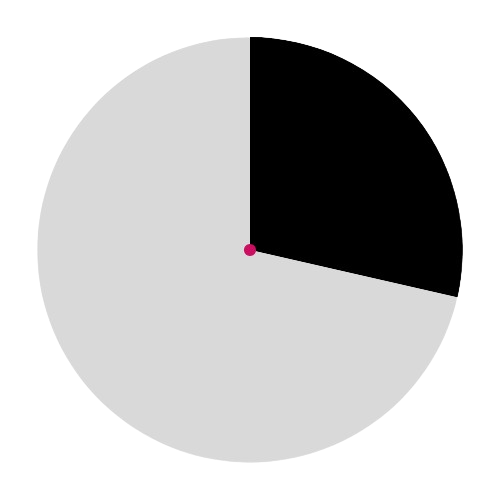
This diagram shows a diameter, not an arc:
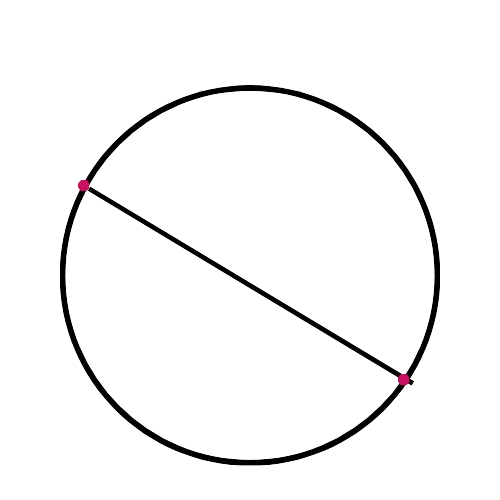
This diagram shows the centre, not an arc:
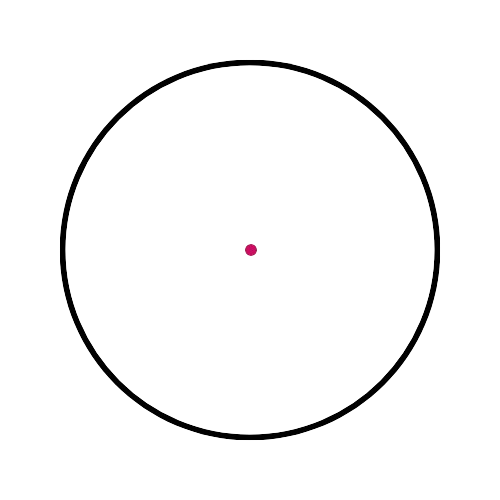
Which figure shows a chord?
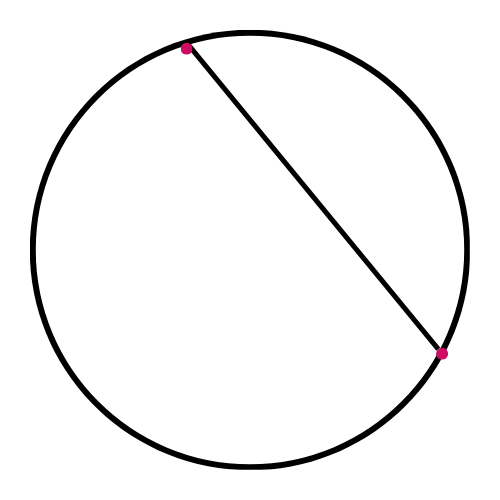
This diagram correctly shows a chord:
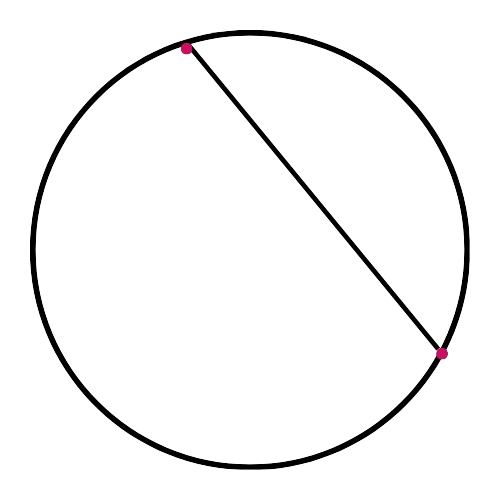
This diagram shows an arc, not a chord:
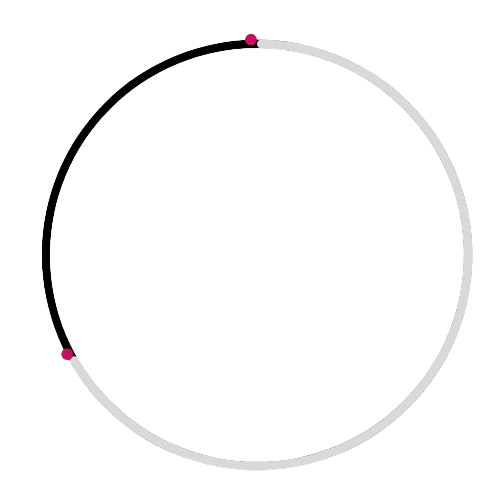
This diagram shows the centre, not a chord:
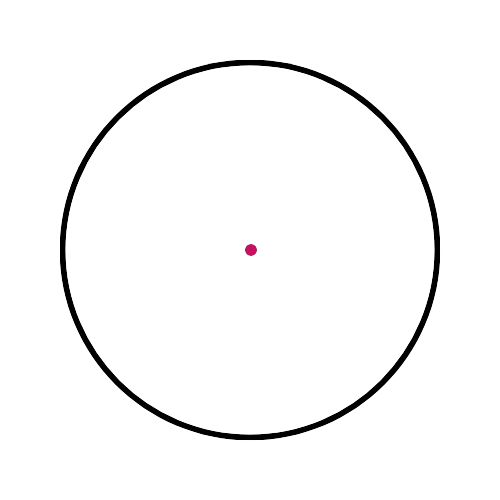
This diagram shows a sector, not a chord:
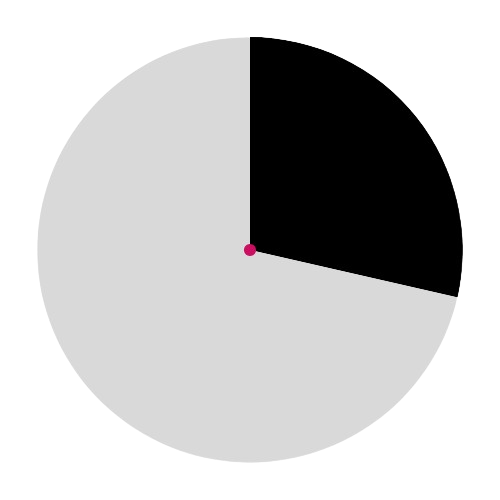
let’s practice!

