Properties of squares and rectangles
key notes :
🔶 🟨 SQUARE – Properties
A square is a special type of rectangle and rhombus. Let’s explore its amazing properties! 💎
1️⃣ All sides are equal 👉 AB = BC = CD = DA
2️⃣ All angles are right angles (90° each) ➡️ ⬜
3️⃣ Opposite sides are parallel ➡️ AB ∥ CD, AD ∥ BC
4️⃣ Diagonals are equal and bisect each other at right angles (90°) ➗
5️⃣ Each diagonal bisects the opposite angles 🔺
6️⃣ Diagonals divide the square into 4 congruent right-angled triangles ✂️
7️⃣ Perimeter = 4 × side 📏
8️⃣ Area = side² 🧮
9️⃣ Symmetry:
- 4 lines of symmetry ✴️
- Rotational symmetry of order 4 🔄
🔷 🟦 RECTANGLE – Properties
A rectangle is a parallelogram with right angles. Let’s see what makes it special! 📐
1️⃣ Opposite sides are equal and parallel ➡️ AB ∥ CD, AD ∥ BC
2️⃣ All angles are 90° (Right angles) ⬜
3️⃣ Diagonals are equal ➗
4️⃣ Diagonals bisect each other (but not at 90°) ❌↕️
5️⃣ Opposite sides are congruent (same length) 📏
6️⃣ Perimeter = 2 × (length + breadth) 🔲
7️⃣ Area = length × breadth 🧮
8️⃣ Symmetry:
- 2 lines of symmetry ✳️
- Rotational symmetry of order 2 🔁
⚖️ 🟩 Difference Between Square and Rectangle
| Property 🧩 | Square 🟨 | Rectangle 🟦 |
|---|---|---|
| Sides | All sides equal | Opposite sides equal |
| Diagonals | Equal and perpendicular | Equal but not perpendicular |
| Angles | All 90° | All 90° |
| Lines of Symmetry | 4 | 2 |
| Example | Chessboard cell ♟️ | Book cover 📖 |
💡 Remember:
Every square is a rectangle ✅ but not every rectangle is a square ❌
Learn with an example
Quadrilateral EFGH is a square. What is ∠DFE?
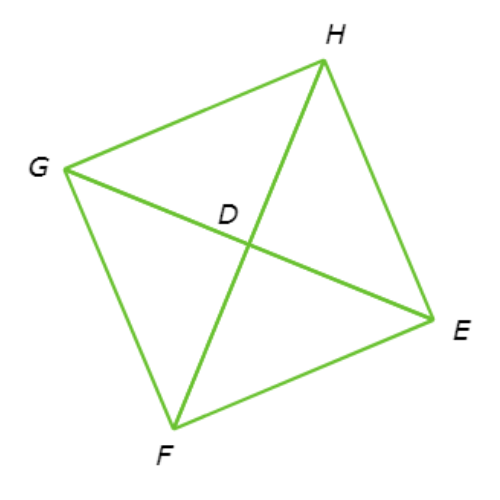
∠DFE= ____°
Since EFGH is a square, ∠EFG=90° and FH bisects ∠EFG.

So, ∠DFE=45°.
Quadrilateral TUVW is a square. What is ∠SWT?
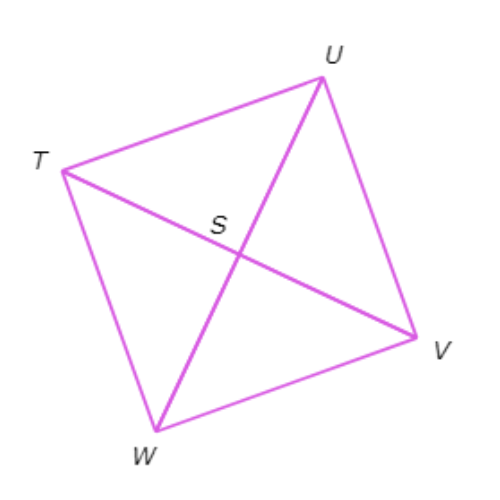
∠SWT= ____°
Since TUVW is a square, ∠TWV=90° and UW bisects ∠TWV.
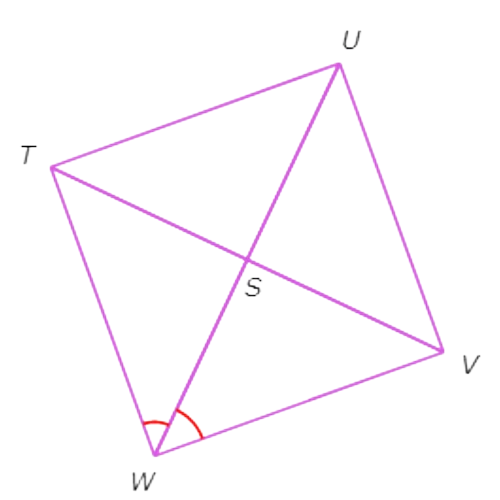
So, ∠SWT=45°.
Quadrilateral CDEF is a square. What is ∠EFG?
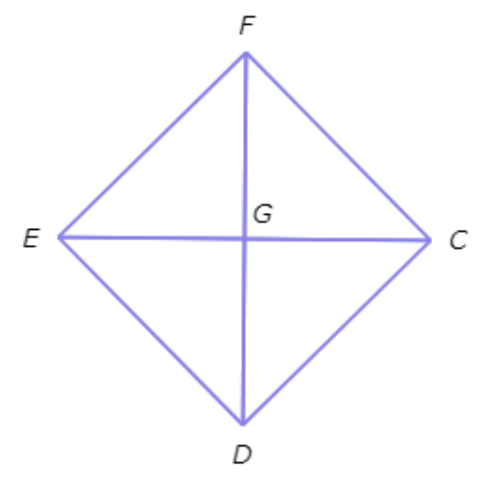
∠EFG= ____°
Since CDEF is a square, ∠CFE=90° and DF bisects ∠CFE.

So, ∠EFG=45°.
Let’s practice!

