Properties of parallelograms
key notes :
🧭 Definition
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral (four-sided figure) where both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
➡️ Example: Rectangle, Rhombus, Square are all types of parallelograms.
📏 Opposite Sides are Equal
👉 In a parallelogram, the opposite sides have the same length.
🟰 AB = CD and AD = BC
✨ This property helps in proving sides equal in geometry problems.
📐 Opposite Angles are Equal
🔁 The angles facing each other in a parallelogram are equal.
🎯 ∠A = ∠C and ∠B = ∠D
➕ Adjacent Angles are Supplementary
🧮 Any two consecutive angles in a parallelogram add up to 180°.
📘 ∠A + ∠B = 180°
💡 This helps in finding missing angle measures!
🔺 Diagonals Bisect Each Other
📏 The diagonals cut each other into two equal halves.
➡️ AO = CO and BO = DO
💎 This is a key property used in coordinate geometry proofs.
🔄 Each Diagonal Divides the Parallelogram into Two Congruent Triangles
✂️ The diagonal splits the parallelogram into two equal-area triangles.
📐 △ABC ≅ △CDA
🧮 Opposite Sides are Parallel
➡️ AB ∥ CD and AD ∥ BC
This is the basic condition for any parallelogram!
💫 Area of a Parallelogram
📏 Area = Base × Height
🧠 Note: The height is the perpendicular distance between the two parallel sides.
🟦 Types of Parallelograms
| Type | Special Property |
|---|---|
| 🔶 Rectangle | All angles are 90° |
| 🔷 Rhombus | All sides are equal |
| ⬜ Square | All sides equal & angles 90° |
🧠 🔟 Key Facts Recap
✅ Opposite sides → Equal & parallel
✅ Opposite angles → Equal
✅ Adjacent angles → Supplementary
✅ Diagonals → Bisect each other
✅ Each diagonal → Forms congruent triangles
💡 Remember:
If any one pair of opposite sides are both equal and parallel, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram! 🟰➡️
Learn with an example
Find the value of c in parallelogram EFGH.
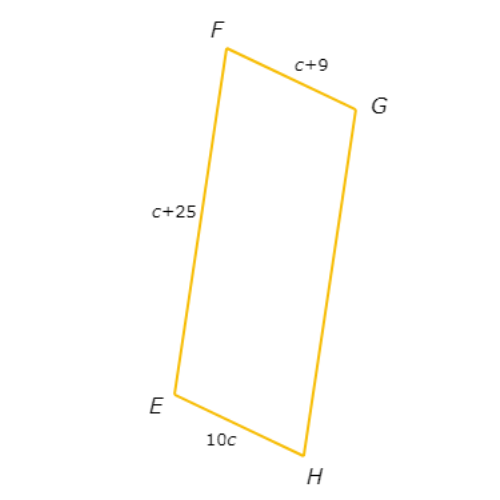
c =________
First, find the pair of opposite sides whose lengths are given in terms of c. The length of EH is 10c and the length of FG is c+9.
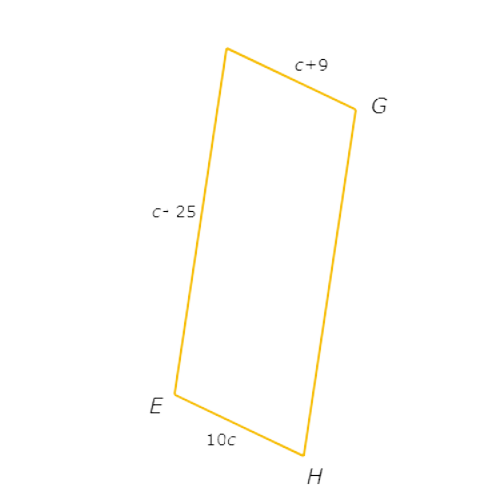
Since opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent, set EH equal to FG and solve for c.
EH = FG
10c = c+9 Plug in EH=10c and FG=c+9
9c = 9 Subtract c from both side
c = 1 Divide both sides by 9
So, c=1.
Find the value of u in rhombus PQRS.
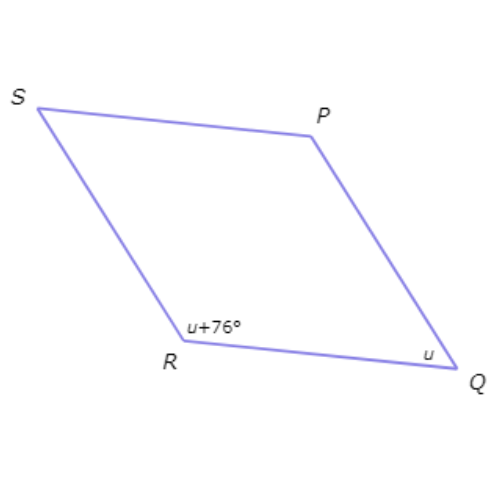
u=____°
First, find the two angles whose measures are in terms of u. The measure of ∠Q is u and the measure of ∠R is u+76°. Notice that ∠Q and ∠R are consecutive angles.
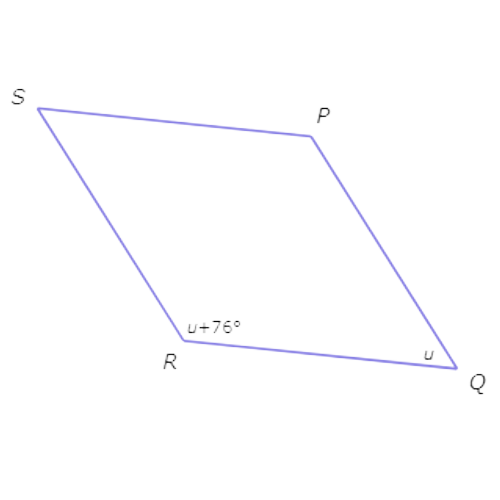
Consecutive angles in a rhombus are supplementary, so set the sum of ∠Q and ∠R equal to 180° and solve for u.
∠Q +∠R = 180°
u + (u + 76°) = 180° Plug in ∠Q = u and ∠R = u + 76°
2u + 76° = 180° Combine like terms
2u = 104° Subtract 76° from both sides
u = 52° Divide both sides by 2
So, u = 52°.
Find the value of t in rhombus PQRS.
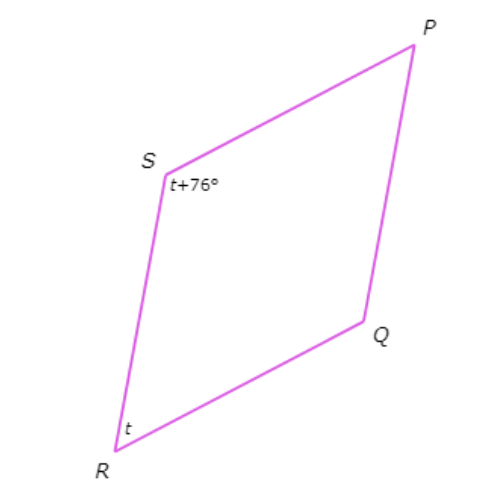
t= _____°
First, find the two angles whose measures are in terms of t. The measure of ∠R is t and the measure of ∠S is t + 76°. Notice that ∠R and ∠S are consecutive angles.
Consecutive angles in a rhombus are supplementary, so set the sum of ∠R and ∠S equal to 180° and solve for t.
∠R + ∠S = 180°
t + (t + 76°) = 180° Plug in ∠R = t and ∠S = t + 76°
2t + 76° = 180° Combine like terms
2t = 104° Subtract 76° from both sides
t = 52° Divide both sides by 2
So, t = 52°.

