SSS Theorem in the coordinate plane
key notes :
📘 🔺 SSS Theorem (Side–Side–Side Theorem)
💡 The SSS Theorem states that:
➡️ If the three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. 🎯
Symbolically:
If AB = DE, BC = EF, and CA = FD,
then △ABC ≅ △DEF. ✅
📏 In the Coordinate Plane 🧮
To apply the SSS Theorem in the coordinate plane:
We use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides of triangles.
🧠 Distance Formula:
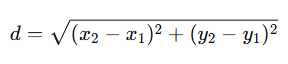
🔹 Steps to Prove SSS Theorem in the Coordinate Plane
1️⃣ Plot the Points on the coordinate plane. 📊
2️⃣ Label the Triangles (e.g., △ABC and △DEF). ✏️
3️⃣ Find the Lengths of all three sides using the distance formula. 📐
4️⃣ Compare the Sides:
- If AB = DE, BC = EF, and CA = FD,
then triangles are congruent by SSS Theorem! 🎉
🧩 Example
Let’s take two triangles:
A(1, 2), B(4, 6), C(5, 2)
and
D(2, 1), E(5, 5), F(6, 1)
👉 Use the distance formula to find all sides.
If all three pairs of sides are equal — ✅
then △ABC ≅ △DEF by SSS Theorem.
🏆 Why It’s Important
✨ Helps us prove triangles are congruent on the coordinate plane.
✨ Used in geometry, computer graphics, and architecture.
✨ Builds the base for proving other geometric properties.
🎨 Quick Recap
🔹 SSS = Side–Side–Side
🔹 Use the distance formula to check sides
🔹 Equal sides → Congruent triangles
🔹 Congruent triangles → Equal corresponding angles
💬 Memory Tip
🧡 “Three sides the same – triangles claim the same name!” 🔺
Learn with an example
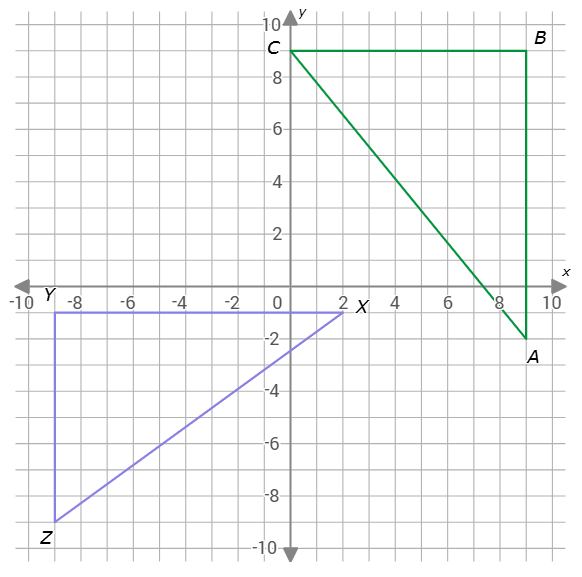
Are △ABC and △XYZ congruent?
- yes
- no
To see that △ABC and △XYZ are not congruent, calculate the three side lengths of each triangle.
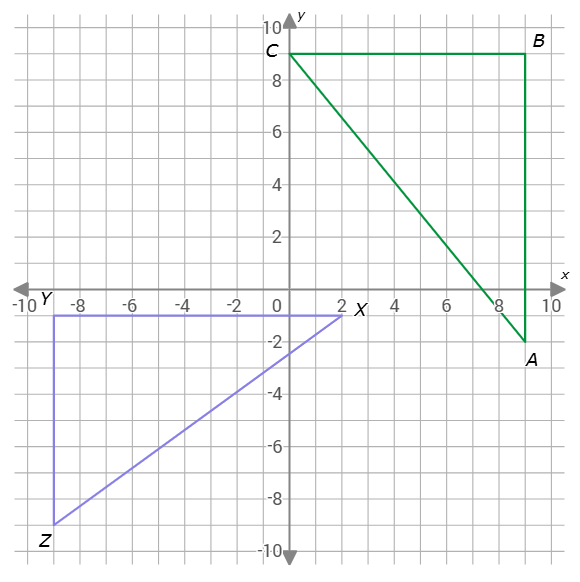
△ABC has vertices A(9,–2), B(9,9) and C(0,9) and △XYZ has vertices X(2,–1), Y(–9,–1) and Z(–9,–9).
Step 1: Find the side lengths of △ABC.
First, find AB. Since A(9,–2) and B(9,9) have the same x-coordinate, AB is the absolute value of the difference in the y-coordinates. So, AB=|9– –2|=11.
Second, find BC. Since B(9,9) and C(0,9) have the same y-coordinate, BC is the absolute value of the difference in the x-coordinates. So, BC=|0–9|=9.
Third, find AC. Since A(9,–2) and C(0,9) do not have equal x-coordinates or equal y-coordinates, use the distance formula to calculate AC. Plug in A(9,–2) for (x1,y1) and C(0,9) for (x2,y2), and simplify.

The three side lengths of △ABC are AB=11, BC=9, and AC=202.
Step 2: Find the side lengths of △XYZ.
First, find XY. Since X(2,–1) and Y(–9 , –1) have the same y-coordinate, XY is the absolute value of the difference in the x-coordinates. So, XY = |– 9 –2| = 11.
Second, find YZ. Since Y(–9,–1) and Z(–9,–9) have the same x-coordinate, YZ is the absolute value of the difference in the y-coordinates. So, YZ = | –9– –1| = 8.
Since no side of △ABC has length 8, YZ is not congruent to AB , BC, or AC. Therefore, △ABC is not congruent to △XYZ by the SSS Theorem.
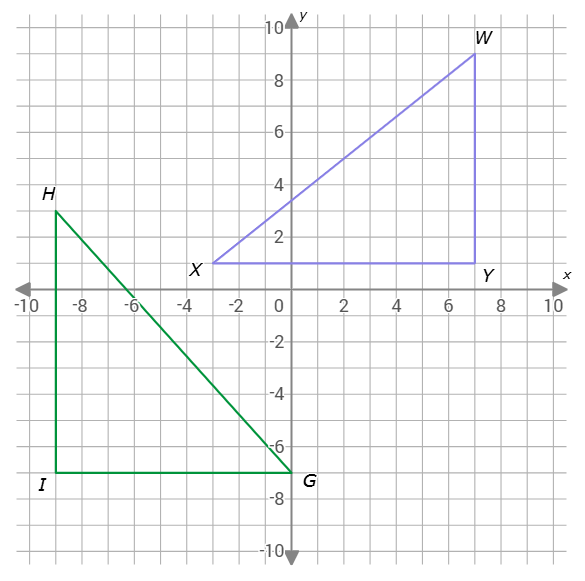
Are △GHI and △WXY congruent?
- yes
- no
To see that △GHI and △WXY are not congruent, calculate the three side lengths of each triangle.

△GHI has vertices G(0,–7), H(–9,3) and I(–9,–7) and △WXY has vertices W(7,9), X(–3,1) and Y(7,1).
Step 1: Find the side lengths of △GHI.
First, find GI. Since G(0,–7) and I(–9,–7) have the same y-coordinate, GI is the absolute value of the difference in the x-coordinates. So, GI=|–9–0|=9.
Second, find HI. Since H(–9,3) and I(–9,–7) have the same x-coordinate, HI is the absolute value of the difference in the y-coordinates. So, HI=|–7–3|=10.
Third, find GH. Since G(0,–7) and H(–9,3) do not have equal x-coordinates or equal y-coordinates, use the distance formula to calculate GH. Plug in G(0,–7) for (x1,y1) and H(–9,3) for (x2,y2), and simplify.

The three side lengths of △GHI are GI=9, HI=10, and GH=181.
Step 2: Find the side lengths of △WXY.
First, find XY. Since X(–3,1) and Y(7,1) have the same y-coordinate, XY is the absolute value of the difference in the x-coordinates. So, XY=|7– –3|=10.
Second, find WY. Since W(7,9) and Y(7,1) have the same x-coordinate, WY is the absolute value of the difference in the y-coordinates. So, WY=|1–9|=8.
Since no side of △GHI has length 8, WY is not congruent to GI , HI, or GH. Therefore, △GHI is not congruent to △WXY by the SSS Theorem.
Let’s Practice!

