Exterior angle inequality
key notes :
🔹 What is an Exterior Angle?
👉 An exterior angle of a triangle is formed when one side of the triangle is extended outward.
📐 Example: If side BC of triangle ABC is extended, then the angle formed outside at C is the exterior angle.
🔹 Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem
💡 The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of its opposite interior angles.
🧠 Statement:
In a triangle, each exterior angle is greater than either of the non-adjacent interior angles.
📊 Symbolically:
If ∠ACD is the exterior angle of triangle ABC,
then 👉 ∠ACD > ∠A and ∠ACD > ∠B
🔹 Explanation with Diagram
Imagine 🔺ABC, where side BC is extended to D.
Then,
- ∠ACD = exterior angle
- ∠A and ∠B = interior opposite angles
So,
➡️ ∠ACD > ∠A
➡️ ∠ACD > ∠B
🔹 Why is it True?
🧩 Because the exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles (Exterior Angle Theorem):
👉 ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B
Since ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B,
it must be greater than each one of them individually.
🔹 Example Problem
If ∠A = 40° and ∠B = 60°,
then the exterior angle (∠ACD) = 40° + 60° = 100°
✅ Therefore,
∠ACD (100°) > ∠A (40°)
∠ACD (100°) > ∠B (60°)
🔹 Key Takeaways 📝
🌟 The exterior angle of a triangle is always:
- Greater than either opposite interior angle.
- Equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles.
- Less than 180° because it forms a linear pair with an interior angle.
💬 Real-Life Connection 🌍
📏 When opening a door 🚪, the angle formed outside the door frame is like an exterior angle, and it’s always larger than the small angles inside!
🎯 Summary Table
| Concept | Description | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Exterior Angle | Formed by extending one side | ∠ACD |
| Interior Opposite Angles | Angles opposite to the exterior angle | ∠A, ∠B |
| Relation | ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B | |
| Inequality | ∠ACD > ∠A and ∠ACD > ∠B | ✅ |
Learn with an example
Which of ∠1, ∠4 and ∠3 has the largest measure?
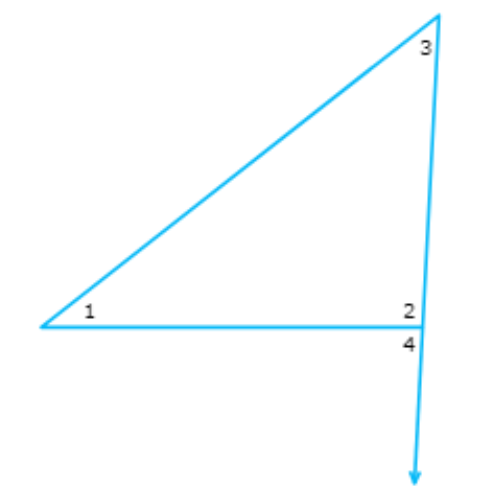
- ∠1
- ∠4
- ∠3
Find ∠1, ∠4 and ∠3 in the diagram.
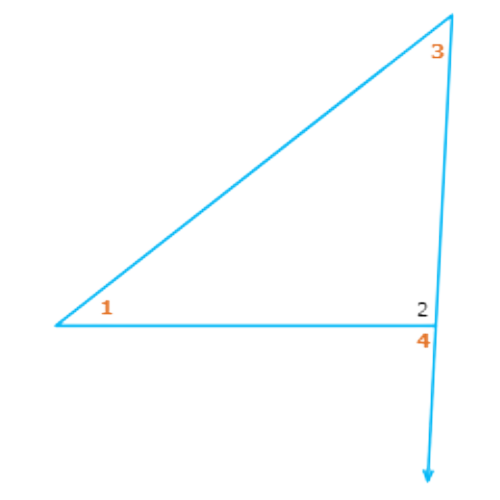
Since ∠4 is an exterior angle of a triangle with ∠1 and ∠3 as remote interior angles, ∠4 is greater than ∠1 and ∠3. So, ∠4 has the largest measure of the three angles.
Which of ∠6, ∠3 and ∠4 has the largest measure?
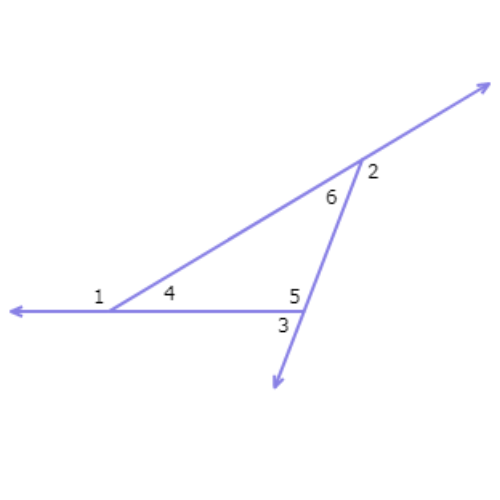
- ∠6
- ∠3
- ∠4
Find ∠6, ∠3 and ∠4 in the diagram.
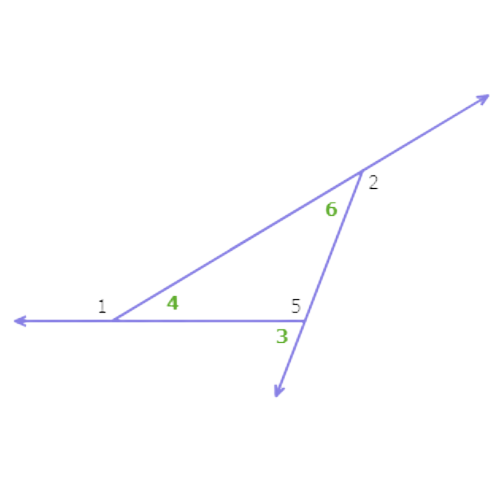
Since ∠3 is an exterior angle of a triangle with ∠4 and ∠6 as remote interior angles, ∠3 is greater than ∠4 and ∠6. So, ∠3 has the largest measure of the three angles.
Which of ∠3, ∠4 and ∠1 has the largest measure?
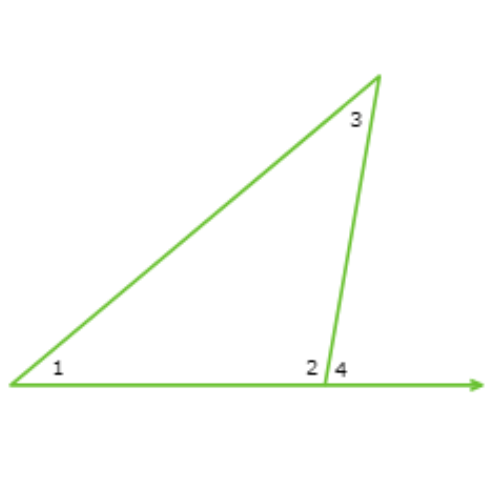
- ∠3
- ∠4
- ∠1
Find ∠3, ∠4 and ∠1 in the diagram.
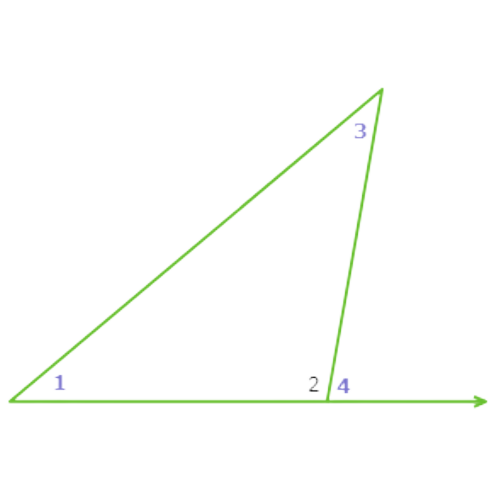
Since ∠4 is an exterior angle of a triangle with ∠1 and ∠3 as remote interior angles, ∠4 is greater than ∠1 and ∠3. So, ∠4 has the largest measure of the three angles.

Let’s practice!

