Exterior angle property
key notes :
🌟 Exterior Angle Property
🧮 What is an Exterior Angle?
- An exterior angle of a triangle is the angle formed outside the triangle when one side of the triangle is extended.
👉 Example: If side BC of triangle ABC is extended to point D, then ∠ACD is an exterior angle.
📏 Exterior Angle Property
👉 The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles.
✨ Formula:
Exterior Angle = Sum of two opposite Interior Angles
🟩 Example:
If in triangle ABC, side BC is extended to D,
then
∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B
💡 Important Notes
- The exterior angle and its adjacent interior angle form a linear pair (sum = 180°).
- There can be three exterior angles in a triangle, one at each vertex.
- The sum of all exterior angles of a triangle (one per vertex) is 360°.
🔢 Example Problem
In △ABC, side BC is extended to D.
If ∠A = 50° and ∠B = 60°,
then
∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B = 50° + 60° = 110°
✅ Answer: 110°
🧠 Real-life Connection
🛣️ The concept of exterior angles helps in:
- Architecture 🏗️ (designing triangular roof structures)
- Navigation 🧭 (finding direction turns)
- Engineering ⚙️ (calculating forces and support angles)
🏁 Summary
| 🟢 Concept | 🧠 Description |
|---|---|
| Exterior Angle | Formed by extending one side of a triangle |
| Property | Exterior angle = sum of two opposite interior angles |
| Linear Pair | Exterior + Adjacent Interior = 180° |
| Sum of all Exterior Angles | 360° |
✨ Remember:
“The outside (exterior) angle always equals the sum of the two far-away (interior) angles!” 💫
Learn with an example
What is ∠1?
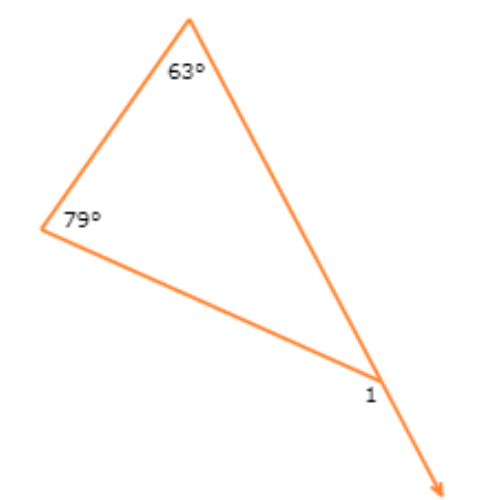
∠1 = ______°
∠1 is an exterior angle of the triangle. The two remote interior angles measure 79° and 63°.
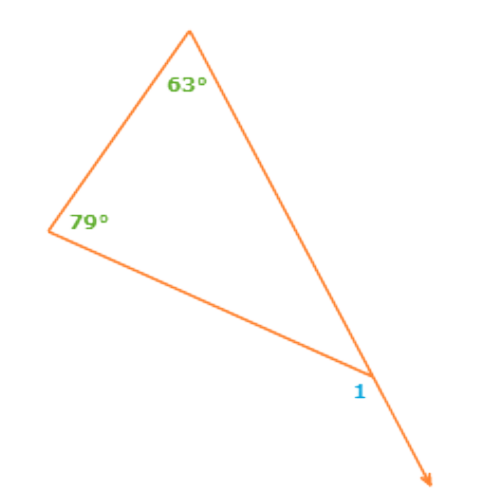
To find the exterior angle measure, add the two remote interior angle measures.
∠1 = 79°+63°
= 142° Add
So, ∠1 = 142°.
What is ∠1?
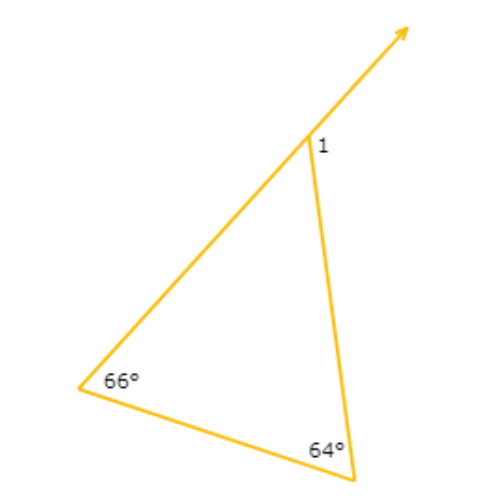
∠1 = ___°
∠1 is an exterior angle of the triangle. The two remote interior angles measure 64° and 66°.
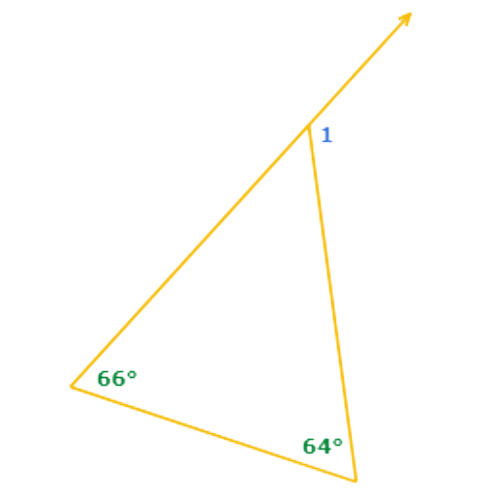
To find the exterior angle measure, add the two remote interior angle measures.
∠1 = 64°+66°
= 130° Add
So, ∠1 = 130°.
What is ∠1?
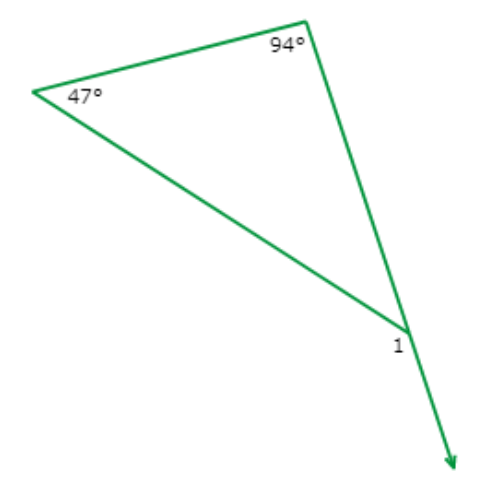
∠1 = ____°
∠1 is an exterior angle of the triangle. The two remote interior angles measure 47° and 94°.
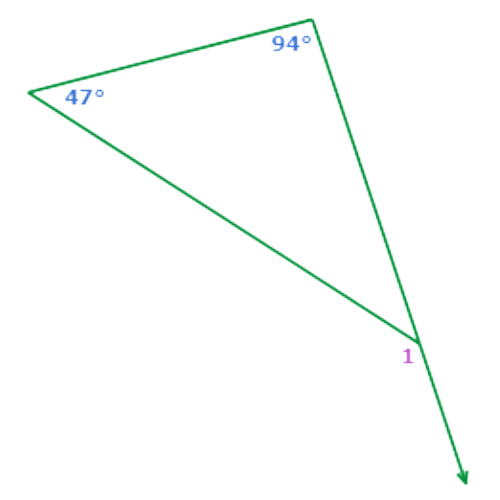
To find the exterior angle measure, add the two remote interior angle measures.
∠1 = 47°+94°
= 141° Add
So, ∠1 = 141°.
Let’s practice!

