Congruency in isosceles and equilateral triangles
key notes :
🔺 What is Congruency?
👉 Two figures are said to be congruent if they have the same shape and size.
🟰 In triangles, congruency means all corresponding sides and angles are equal.
👯♂️ Isosceles Triangle
📘 Definition: A triangle with two sides of equal length and the angles opposite those sides are also equal.
💡 Example: If AB=AC, then ∠B=∠C.
💠 Congruency in Isosceles Triangles
⭐ If two sides of a triangle are equal,
then the angles opposite those sides are also equal.
📏 Similarly, if two angles are equal,
then the sides opposite those angles are equal.
🧩 Hence, the two base angles are congruent!
🔹 Congruency Criteria for Isosceles Triangles
🧮 You can use any of the triangle congruence rules:
✅ SSS (Side-Side-Side)
✅ SAS (Side-Angle-Side)
✅ ASA (Angle-Side-Angle)
✅ AAS (Angle-Angle-Side)
✅ RHS (Right angle-Hypotenuse-Side)
🔷 Equilateral Triangle
📘 Definition: A triangle with all sides equal and all angles equal (each 60°).
🟰 Every equilateral triangle is also isosceles (because it has at least two equal sides).
💫 Congruency in Equilateral Triangles
⭐ Any two equilateral triangles are congruent if one side of one equals one side of the other.
🧠 Reason: All sides and all angles are equal in an equilateral triangle!
🧭 Important Properties Summary
| 🔹 Property | 🔸 Isosceles Triangle | 🔸 Equilateral Triangle |
|---|---|---|
| Equal sides | 2 sides | 3 sides |
| Equal angles | 2 angles | 3 angles (each 60°) |
| Line of symmetry | 1 | 3 |
| Congruency condition | Base angles or sides equal | One side equal is enough |
💖 Real-Life Examples
🏠 Roofs of houses (isosceles triangles)
🎈 Triangular road signs (equilateral triangles)
🎪 Decorative patterns, flags, and logos
🎯 Key Takeaway
👉 All equilateral triangles are isosceles, but not all isosceles triangles are equilateral!
✨ Congruency helps us prove equality in sides and angles of these triangles.
Learn with an example
What is the value of p?
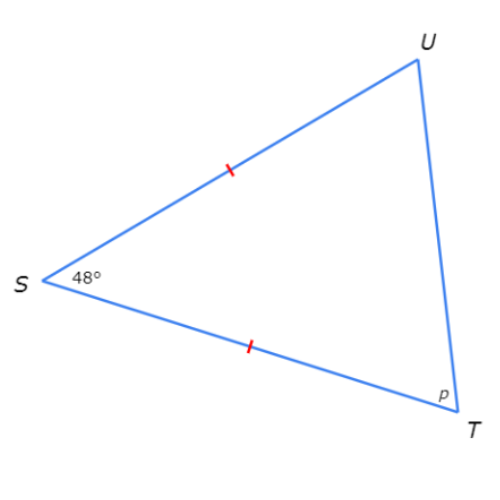
p =
Look at the diagram.
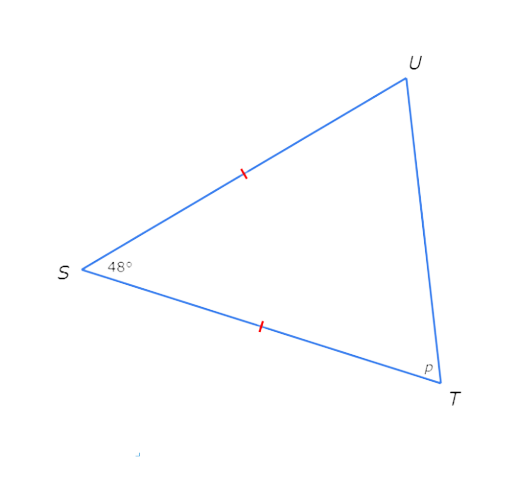
ST and SU are marked with one hatch mark each. So, they are congruent. By the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, the angles opposite ST and SU must also be congruent.
The angle opposite ST is ∠U and the angle opposite SU is ∠T. So, ∠U and ∠T have the same measure. From the diagram you can see that ∠T=p, so ∠U=p as well.
Now, set the sum of the interior angle measures of △STU equal to 180° and solve for p.
∠S+∠T+∠U = 180°
48°+p+p = 180° —-> Plug in ∠S=48°, ∠T=p and ∠U=p
2p+48° = 180° —–> Combine like terms
2p = 132° ——>Subtract 48° from both sides
p= 66° ——->Divide both sides by 2
So, p=66°.
What is the value of a?
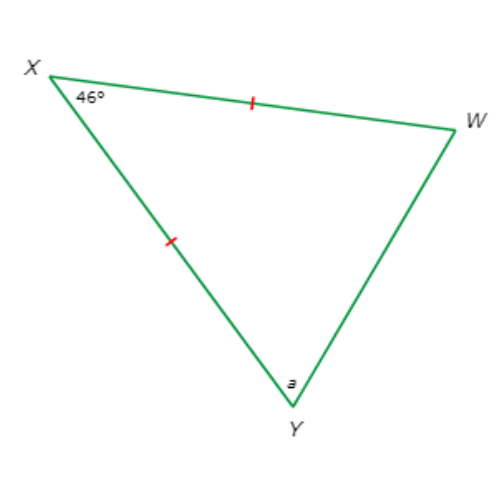
a= ______°
Look at the diagram.

WX and XY are marked with one hatch mark each. So, they are congruent.
By the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, the angles oppositeWX and XY must also be congruent.
The angle opposite WX is ∠Y and the angle opposite XY is ∠W. So, ∠Y and ∠W have the same measure. From the diagram you can see that ∠Y=a, so ∠W=a as well.
Now, set the sum of the interior angle measures of △WXY equal to 180° and solve for a.
∠W+∠X+∠Y = 180°
a+46°+a = 180° Plug in ∠W=a, ∠X=46° and ∠Y=a
2a+46° = 180° Combine like terms
2a = 134° Subtract 46° from both sides
a = 67° Divide both sides by 2
So, a=67°.
What is the value of w?
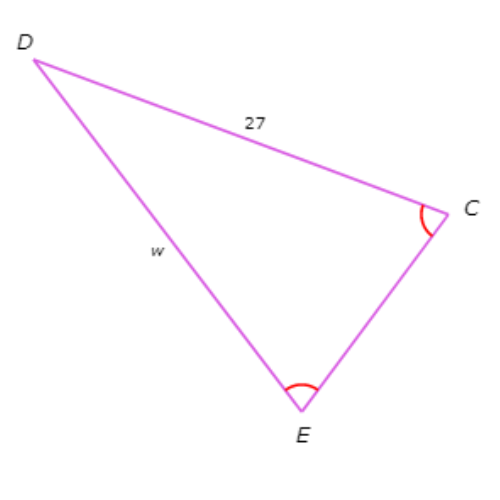
w=
Look at the diagram.
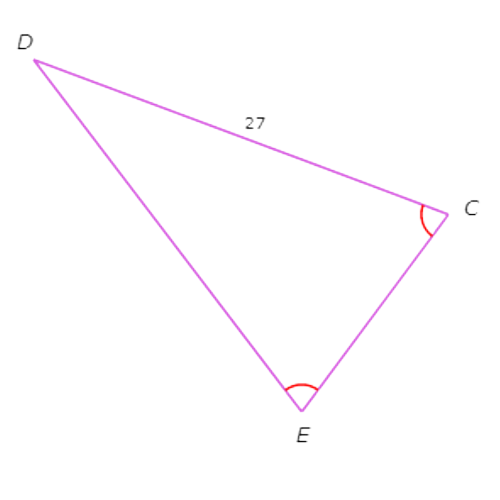
∠C and ∠E are marked with one arc each. So, they are congruent.
By the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, the sides opposite ∠C and ∠E must also be congruent.
The side opposite ∠C is DE and the side opposite ∠E is CD . So, DE and CD have the same length. From the diagram you can see that the length of CD is 27 and the length of DE is w.
For these to be the same, w must equal 27.
Let’s try some problems!✍️

